MCQ of Chemistry CUET | Common University Entrance Test |
Table of Contents
MCQ of Chemistry CUET | Common University Entrance Test |
MCQ of The Solid State
Question 1: Ionic solids conduct electricity in molten state but not in solid state because
- In molten state free ions are furnished which are not free to move in solid state
- In solid state, ionic solids are hard , brittle and become soft in molten state
- All solids conduct electricity in molten state
- in solid state, ions are converted to atoms which are insulators
Answer: A (In molten state free ions are furnished which are not free to move in solid state)
Question 2: What type of solid is SiC ?
- Covalent or network solid
- Metallic solid
- Ionic solid
- Molecular solid
Answer: A (Covalent or network solid)
Question 3 : Name one solid which has both Schottky and Frenkel defects.
- Silver Chloride
- Silver Bromide
- Cesium Chloride
- Zince Blende
Answer: B (Silver bromide)
Question 4 : What is the coordination number of an octahedral void ?
- Four
- Eight
- Six
- None of these
Answer: C (Six)
Question 5 : What type of interaction hold the molecules together in a polar molecular solid ?
- Van der Waals force
- Hydrogen Bonding
- Columbic Force
- Dipole – dipole interaction
Answer: D (Dipole- dipole interaction)
Question 6 : In a crystal of zinc sulphide, zinc occupies tetrahedral voids. What is the coordination number of zinc?
- Four
- Six
- Eight
- None of these
Answer: A (Four)
Question 7: Arrange the following according to their packing fractions: Simple cubic, Face centred cubic, body centred cubic
- Body centred < face centred < Simple
- Simple < body centred < face centred
- Simple < face centred < body centred
- Face centred < simple < body centred
Answer: B (Simple < body centred < face centred)
Question 8: Name the type of point defect that occurs in a crystal of zinc sulphide.
- Schottky defect
- Vacancy defect
- Frenkel defect
- Metal deficiency defect
Answer: C (Frenkel defect)
Question 9: Which point defect in crystals of a solid does not change the density of the solid?
- Frenkel defect
- Vacancy defect
- Schottky defect
- Metal deficiency defect
Answer: A (Frenkel defect)
Question 10: What is the cause of electrical conductivity in metals ?
- Due to flow of electrons
- Due to flow of ion in solution
- Due to presence of impurities and defects
- None of these
Answer: A (Due to flow of electrons)
Question 11: What is the percentage of empty space in a body centred cubic arrangement?
- 54 %
- 68 %
- 32%
- 74 %
Answer: C (32 %)
Question 12: If the radius of an octahedral void is r and radius of atom in close packing is R, the relation between r and R is
- r = 0.732 R
- r = 0.414 R
- r = 0.225 R
- None of these
Answer: B (r = 0.414 R)
Question 13: Solid X is a very hard solid which is electrical insulator in solid as well as in molten state and has extremely high boiling point. What type of solid is it?
- Ionic Solid
- Metallic Solid
- Molecular Solid
- Covalent solid
Answer: D (Covalent solid)
Question 14: What type of substance would make better permanent magnets
- Ferromagnetic
- Ferrimagnetic
- Anti- ferrimagnetic
- Paramagnetic
Answer: A (Ferromagnetic)
Question 15: What is two dimensional coordination number of a molecule in square close- packed structure?
- 4
- 6
- 12
- 8
Answer: A (4)
Question 16: How does the electrical conductivity of semiconductors vary with temperature?
- Decreases
- Increases
- Remain unchanged
- None of these
Answer: B (Increases)
Question 17: A crystal is made of particles X and Y, X forms fcc packing and Y occupies all the octahedral voids. If all the particles along one bond diagonal are removed then the formula of crystal would be
- X4Y3
- X5Y4
- X4Y5
- none of these
Answer: B (X5Y4 )
Question 18: How does the electrical conductivity of metallic conductors vary with temperature?
- Remain Unchanged
- Increases
- Decreases
- None of these
Answer: C (Decreases)
Question 19: Which of the following does not represent a crystal system?
- Triclinic
- Monoclinic
- Rhombohedral
- Isotropical
Answer: C (Isotropical)
Question 20: In a schottky defect
- An ion moves to interstitial position between the lattice points
- Electrons are trapped in a lattice site
- Some lattice sites are vacant
- Some extra cations are present in interstitial spaces
Answer: D (Some lattice sites are vacant)
Question 21: To get n type semiconductor, germanium should be doped with
- Gallium
- Arsenic
- Aluminium
- Boron
Answer: B (Arsenic)
Question 22: Which of the following statements is not true about the voids?
- Octahedral void is formed at centre of six spheres which lie at the apices of a regular octahedron.
- There is one octahedral site for each sphere.
- There are two tetrahedral sites for each sphere.
- Octahedral voids are formed when triangular voids in second layer exactly overlap with similar voids in the first layer.
Answer: A (Octahedral voids are formed when triangular voids in second layer exactly overlap with similar voids in the first layer.)
Question 23: If three elements, X, Y and Z crystallise in a ccp lattice with X atoms at the corners, Y atoms at the cube centre and Z atoms at the edges, the formula of the compound will be
- XYZ
- XYZ2
- XYZ3
- X2Y2Z
Answer: C (XYZ3)
Question 24: Silver halides generally show
- Schottky defect
- Frenkel defect
- Both Frenkel and Schottky defect
- Cation excess defect
Answer: C (Both Frenkel and Schottky defect)
Question 25: Which of the following will have metal deficiency defect?
- NaCl
- FeO
- KCl
- ZnO
Answer: B (FeO)
Question 26: Pure silicon and germanium behave as
- Conductors
- Semiconductors
- Insulators
- Piezoelectric crystals
Answer: C (Insulators)
Question 27: Which of the following crystals does not exhibit Frenkel defect?
- AgBr
- AgCl
- KBr
- ZnS
Answer: C (KBr)
Question 28: An electron trapped in an anionic site in a crystal is called
- F-centre
- Frenkel defect
- Schottky defect
- interstitial defect
Answer: A (F-centre)
Question 29: The edge length of fcc cell is 508 pm. If radius of cation is 110 pm, the radius of anion is
- 110 pm
- 220 pm
- 285 pm
- 144 pm
Answer: D (144 pm)
Question 30: Alkyl halides do not show Frenkel defect because
- Cations and anions have almost equal size
- There is a large difference in size of cations and anions
- Cations and anions have low coordination number
- Cnions cannot be accommodated in voids
Answer: C (Cations and anions have almost equal size)
MCQ of Solutions
Question 1: State the main advantage of molality over molarity as the unit of concentration.
- Molality does not change with change in temperature
- Molality changes with temperature
- Molarity changes with temperature
- None of these
Answer: A (Molality does not change with change in temperature )
Question 2: Brass is
- Solid Solution
- Liquid Solution
- Gas solution
- All of these
Answer: A (Solid Solution)
Question 3: Which of the following is an example of solid in gas solution?
- Humidity in air
- Iodine vapour in air
- Alloys
- Air
Answer: B (Iodine vapour in air)
Question 4: Write the relation between normality and molarity of a given solution of H2SO4 ?
- Normality = 2 x Molarity
- Molarity = 2 x Normality
- Normality = 3/4 Molarity
- Molarity = 1/2 Normality
Answer: A (Normality = 2 x Molarity)
Question 5: What is sum of mole fraction of all the components in a three component system?
- x1 + x2 + x3 = 2
- x1 + x2 + x3 = 1
- x1 + x2 = 1
- x1 + x3 = 1
Answer: B (x1 + x2 + x3 = 1 )
Question 6: At equilibrium the rate of dissolution of a solid solute in a volatile liquid solvent is..
- zero
- less than the rate of crystallisation
- equal to the rate of crystallisation
- greater than the rate of crystallisation
Answer: C (Equal to the rate of crystallisation )
Question 7: What do you mean by saying that molality of a solution is 0.1?
- 0.1 mol of solute is dissolved in 1000kg of solvent
- 0.1 mol of solute is present in 100 ml of solution
- 0.1 mol of solute is dissolved in 1000g of solvent
- None of these
Answer: C (0.1 mol of solute is dissolved in 1000 g of solvent)
Question 8: Which has the least freezing point?
- 1% Sucrose
- 1% NaCl
- 1% CaCl2
- 1% Glucose
Answer: C (1% CaCl2 )
Question 9: Which of the following is not a colligative property?
- Depression in freezing point
- Osmotic Pressure
- Elevation in boiling point
- Increase in freezing point
Answer: D (Increase in freezing point)
Question 10: In which of the following condition reverse osmosis takes place ?
- E ext > Osmotic pressure
- E ext = Osmotic pressure
- E ext < Osmotic pressure
- None of these
Answer: A (Eext > Osmotic Pressure)
Question 11: Molarity of a given orthophosphoric acid solution is 3M. Its normality is
- 0.3 N
- 9 N
- 1 N
- 3 N
Answer: B (9 N)
Question 12: What is ebullioscopic constant.
- Elevation in boiling point that take place when molarity of the solution is unity.
- Depression in freezing point that take place when molality of the solution is unity
- Elevation in boiling point that take place when molality of the solution is unity.
- Depression in freezing point that take place when molarity of the solution is unity
Answer:C (Elevation in boiling point that take place when molality of the solution is unity.)
Question 13: Two liquids A and B on mixing produce a warm solution. Which type of deviation from Raoult’s law does it show?
- negative deviation.
- positive deviation
- Ideal solution
- All of these
Answer: A (Negative deviation)
Question 14: A beaker contains a solution of substance A. Precipitation of substance A takes place when small amount of A is added to solution. The solution is ……..
- Saturated
- Unsaturated
- Supersaturated
- None of these
Answer: C (Supersaturated)
Question 15: Maximum amount of a solute that can be dissolved in a specified amount of given liquid solvent does not depend upon
- Pressure
- Temperature
- Nature of solute
- Nature of solvent
Answer: A (Pressure)
Question 16: What happens when blood cells are placed in pure water?
- blood cells shrink
- blood cells swell and may even burst.
- Both of these
- None of these
Answer: B (Blood cells swell and may even burst )
Question 17: When is the value of van’t Hoff factor more than one?
- when solute undego association in the solution
- when the solute undergo dissociation in the solution
- when solute is volatile
- None of these
Answer: B (When the solute undergo dissociation in the solution)
Question 18: Which one has a lowest freezing point?
- 2 M glucose solution
- 1.5 M glucose solution
- 1 M glucose solution
- All of these
Answer: A (2 M glucose solution)
Question 19: Isotonic solutions are solutions having the same
- Vapour pressure
- Surface tension
- Osmotic pressure
- Viscosity
Answer: C (Osmotic Pressure)
Question 20: How is the colligative property of solution changed when a solute in solution undergoes association
- Increases
- Remain same
- Become twice
- Decreases
Answer: D (Decreases)
Question 21: The value of Henry’s constant is…..
- greater for gases with higher solubility
- greater for gases with lower solubility
- constant for all gases
- not related to the solubility of gases
Answer: B (Greater for gases with lower solubility)
Question 22: Vapour pressure of a dilute aqueous solution of glucose is 750 mm of mercury at 373 K. The mole fraction of solute is
- 1 / 76
- 1 / 7.6
- 1 / 38
- 1 / 10
Answer: A (1 / 76) [ Hint : ps = pº1 ( 1- x2) ]
Question 23: The decreasing order of osmotic pressure of 10 g glucose (P 1), 10 g urea (P2) and 10 g sucrose (P3) at 273 K when dissolved in 250 mL of water separately is
- P1 > P2 > P3
- P2 > P3 > P1
- P2 > P1 > P3
- P3 > P2 > P1
Answer: C (P2 > P1 > P3 ) [ Hint : P ∝ 1 / Molar mass ]
Question 24: An azeotropic mixture of two liquids has boiling point lower than either of them when it
- shows negative deviation from Raoult’s law
- shows no deviation from Raoult’s law
- shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law
- is saturated
Answer: C (Shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law)
Question 25: A graph showing the variation of osmotic pressure versus molar concentration of an aqueous solution at temperature T is given below; the slope of the line represent
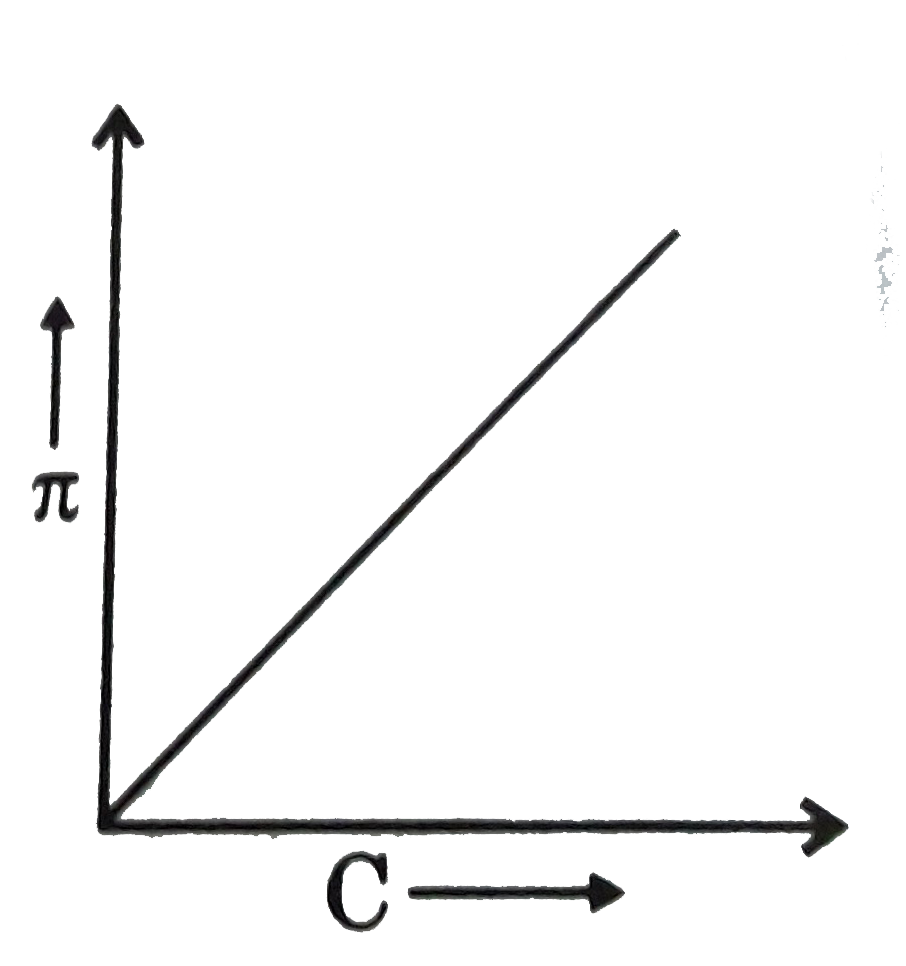
- solution constant R
- absolute temperature T
- RT
- degree of ionization of solute
Answer: C (RT)
Question 26: The osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous solution of NaCl is …… osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous solution of glucose
- equal to
- less than
- half of
- nearly double
Answer: D (Nearly double)
Question 27: Which of the following 0.1 M aqueous solution is likely to have the highest boiling point?
- Na2SO4
- KCl
- Glucose
- Urea
Answer: A (Na2SO4)
Question 28: Increasing the temperature of an aqueous solution will cause
- decrease in molality
- decrease in molarity
- decrease in mole fraction
- decrease in % w/w
Answer: B (Decrease in molarity )
Question 29: Van’t Hoff factor for 0.1 M ideal solution is
- 0.1
- 1
- -0.01
- none of these
Answer:B (1)
Question 30: Which of the following will show negative deviation from Raoult’s law?
- Acetone – benzene
- Acetone – ethanol
- Benzene – methanol
- Acetone – chloroform
Answer: D (Acetone – chloroform)
MCQ of Electrochemistry
Question 1: A standard hydrogen electrode has a zero potential because
- Hydrogen can be most easily oxidised
- Hydrogen has only one electron
- The electrode potential is assumed to be zero
- Hydrogen is the lightest element
Answer: C (The electrode potential is assumed to be zero)
Question 2: Fluorine is the best oxidising agent because it has
- Hydrogen electron affinity
- Highest reduction potential
- Highest oxidation potential
- Lowest electron affinity
Answer: B (Highest reduction potential)
Question 3: Which of the following is not an application of electrochemical series?
- To compare the relative oxidising and reducing power of substances
- To predict evolution of hydrogen gas on reaction of metal with acid
- To predict spontaneity of redox reaction
- To calculate the amount of metal deposited on cathode
Answer: D (To calculate the amount of metal deposited on cathode)
Question 4: Cell reaction is spontaneous, when
- Eºred is negative
- ΔGº is negative
- Eºoxd is positive
- ΔGº is positive
Answer: B (ΔGº is negative)
Question 5: The molar conductivity is maximum for the solution of concentration
- 0.004 M
- 0.002 M
- 0.005 M
- 0.001 M
Answer: D (0.001 M)
Question 6: When water is added to an aqueous solution of an electrolyte, what is change in specific conductivity of the electrolyte?
- Conductivity decreases
- Conductivity increases
- Conductivity remains same
- Conductivity does not depend on number of ions
Answer: A (Conductivity decreases)
Question 7: How much metal will be deposited when a current of 12 ampere with 75% efficiency is passed through the cell for 3 h? (Given : Z = 4 x 10 -4)
- 32.4 g
- 38.8 g
- 36.0 g
- 22.4 g
Answer: B (38.8 g)
Question 8: If 54 g of silver is deposited during an electrolysis reaction, how much aluminium will be deposited by the same amount of electric current?
- 2.7 g
- 4.5 g
- 27 g
- 5.4 g
Answer: B (4.5 g)
Question 9: How much electricity in terms of Faraday is required to produce 100 g of Ca from molten CaCl2 ?
- 1 F
- 2 F
- 3 F
- 5 F
Answer: D (5 F)
Question 10: When a lead storage battery is discharged ,
- lead sulphate is consumed
- oxygen gas is evolved
- lead sulphate is formed
- lead sulphide is formed
Answer: C (lead sulphate is formed)
Question 11: The amount of chlorine evolved by passing 2 A of current in an aqueous solution of NaCl for 30 minute is
- 2.64 g
- 1.32 g
- 3.62 g
- 4.22 g
Answer: B (1.32 g)
Question 12: A galvanic cell has an electrical potential of 1.1 V. If an opposing potential of 1.1 V is applied to this cell, what will happen to cell reaction and current flowing through the cell?
- The reaction stops and no current flows through the cell
- The reaction continues but current flows in opposite direction.
- The concentration of reactants becomes unity and current flows from cathode to anode
- The cell does not function as galvanic cell and zinc is deposited on zinc plate
Answer: A (The reaction stops and no current flows through the cell)
Question 13: Specific conductance of 0.1 M NaCl solution is 1.01 x 10 -2 ohm-1 cm-1. Its molar conductance in ohm -1 cm2 mol-1 is
- 1.01 x 102
- 1.01 x 103
- 1.01 x 104
- 1.01
Answer:A (1.01 x 102)
Question 14: In an electrolytic cell, the flow of electron is
- From cathode to anode in the solution
- From cathode to anode through external supply
- From cathode to anode through internal supply
- From anode to cathode through internal supply
Answer: C (from cathode to anode through internal supply)
Question 15: Which of the following is not a non-electrolyte?
- Acetic acid
- Glucose
- Ethanol
- Urea
Answer: A (Acetic acid )
Question 16: In electrolysis of dilute H2SO4, what is liberated at anode?
- H2
- SO4 2-
- SO2
- O2
Answer: D (O2)
Question 17: Which of the following statements is correct regarding variations of molar conductivity with concentration?
- Molar conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration
- Variation in molar conductivity of weak and strong electrolyte is same
- Molar conductivity increases with decrease in concentration
- When concentration of the solution approaches zero, molar conductivity is known as conductance
Answer: C (Molar conductivity increases with decrease in concentration)
Question 18: The time required to liberate one gram equivalent of an element by passing one ampere current through its solution is
- 6.7 hrs
- 13.4 hrs
- 19.9 hrs
- 26.8 hrs
Answer: D (26.8 hrs)
Question 19: Electrical conductance through metals is called metallic or electronic conductance and is due to the movement of electrons. The electronic conductance depends on
- The nature and structure of the metal
- The number of valence electrons per atom
- Change in temperature
- All of these
Answer: D (all of these)
Question 20: The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called….
- Cell potential
- Cell emf
- Potential difference
- Cell voltage
Answer: B (cell emf)
MCQ of Chemical Kinetics
Question 1: How does concentration of reaction change with time for a chemical reaction ?
- Increases
- Remain Unchanged
- Decreases
- Becomes twice
Answer: C (Decreases)
Question 2: The rate constant of a reaction is 3 x 10 2 min -1 . What is the order of the reaction?
- First
- Second
- Third
- Zero
Answer: A (First)
Question 3: For a reaction R→P, half life (t 1/2) is observed to be independent of the initial concentration of reactants. What is the order of reaction?
- Zero
- First
- Second
- None of these
Answer: B (First)
Question 4: A reaction in which reactants are converted into products follows second order kinetics. If concentration of R is increases by four times, what will be the increase in rate of formation of P?
- 9 times
- 4 times
- 16 times
- 8 times
Answer: C (16 times)
Question 5: The order of reaction is decided by
- Temperature
- Mechanism of reaction as well as relative concentration of reactants
- Molecularity
- Pressure
Answer: B (Mechanism of reaction as well as relative concentration of reactants)
Question 6: Which of the following for order of reaction is not correct?
- Order can be determined experimentally
- Order of reaction is equal to the sum of powers of concentration term in rate law expression.
- Order cannot be fractional
- Order is not affected by stoichiometric coefficient of the reactants.
Answer: C (Order cannot be fractional)
Question 7: A reaction is of second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected, if the concentration of reaction is reduced to half?
- 4 times
- 1/4 times
- 16 times
- Remain unchanged
Answer: B (1/4 times)
Question 8: For a chemical reaction , R→P, the variation in concentration of R with time pot is given as below, predict the order of reaction?

- Zero order
- First order
- Second order
- Insufficient information
Answer: A (zero order)
Question 9: For a reaction A+ B → P, the rate law is given by , r = k[A]1/2 [B]2 . What is the order of this reaction?
- 1/2
- 2
- 5/2
- 3/2
Answer: C (5/2)
Question 9: The overall rate of reaction is governed by
- The rate of fastest intermediate step
- The sum of the rates of all intermediate steps
- The average of the rates of all the intermediate steps
- The rate of slowest intermediate step
Answer: D (The rate of slowest intermediate step)
Question 10: Under what conditions a bimolecular reaction may be of first order?
- When both reactants have same concentration.
- When one of the reacting species is in large excess.
- When the reaction is at equilibrium.
- When the activation energy of reaction is less.
Answer: B (When one of the reacting species is in large excess. )
Question 11: In pseudo unimolecular reactions,
- Both the reactants are present in low concentration
- Both the reactants are present in same concentration
- One of the reactant is present in excess
- One of the reactant is non reactive
Answer: C (one of the reactant is present in excess)
Question 12: When a catalyst is used in an equilibrium process
- It increases the rate of forward reaction
- It decreases the rate of backward direction
- It decreases activation energy of both forward and backward direction
- It fastens the attainment of equilibrium by lowering activation energy.
Answer: D (It fastens the attainment of equilibrium by lowering activation energy.)
Question 13: Half life period of a first order reaction is 10 min. What percentage of the reaction will be completed in 100 min?
- 25%
- 50%
- 99.9%
- 75%
Answer: C (99.9%)
Question 14: Threshold energy is equal to
- Activation energy
- Activation energy – energy of molecules
- Activation energy + energy of molecules
- None of these
Answer: C (Activation energy + energy of molecules)
Question 15: The unit of rate and rate constant are same for a
- Zero order reaction
- First order reaction
- Second order reaction
- Third order reaction
Answer: A (Zero order reaction)
Question 16: The number of molecules of the reactants taking place in a single step of the reaction is indicative of
- Order of reaction
- Molecularity of reaction
- Fast step of the mechanism of reaction
- Half life of the reaction
Answer: B (molecularity of reaction)
Question 17: What will be the rate equation for the reaction 2 X + Y → Z, if the order of the reaction is zero?
- Rate = k[X][Y]
- Rate = k
- Rate = k[X]0[Y]
- Rate =k[X][Y]0
Answer: B (Rate = k)
Question 18: For a reaction X → Y, the rate of reaction becomes twenty seven times when the concentration of X is increases three times. What is order of the reaction?
- 2
- 1
- 3
- 0
Answer: C (3)
Question 19: The rate constant of a reaction depends upon
- Temperature of the reaction
- Extent of the reaction
- Initial concentration of the reactants
- The time of completion of reaction
Answer: A (Temperature of the reaction)
Question 20: The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10ºC rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50ºC , the rate of the reaction increases by about:
- 24 times
- 32 times
- 64 times
- 10 times
Answer: B (32 times )
Question 21: In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction….
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains unchanged
- May increase or decrease
Answer: C (Remains unchanged)
Question 22: The increase in concentration of the reactants lead to change in
- ΔH
- Collision frequency
- Activation energy
- Equilibrium constant
Answer: B (Collision frequency)
Question 23: For an endothermic reaction, ΔH represents the enthalpy of reaction. The minimum amount of activation energy will be
- Less than zero
- Equal to ΔH
- Less than ΔH
- More than ΔH
Answer: D (More than ΔH)
Question 24: The chemical reaction in which reactant require high amount of activation energy are generally
- Slow
- Fast
- Instantaneous
- None of these
Answer: A (Slow)
Question 25: Collision theory is applicable to
- First order reactions
- Zero order reactions
- Bimolecular reactions
- Intramolecular reactions
Answer: C (Bimolecular reactions)
MCQ of Surface Chemistry
Question 1: What type of interface cannot be obtained?
- Gas – Gas
- Solid – liquid
- Liquid – Gas
- Liquid – Liquid
Answer: A (Gas – Gas)
Question 2: Name the process by which freshly prepared precipitate gets converted to colloidal solution?
- Coagulation
- Electrolysis
- Diffusion
- Peptisation
Answer: D (Peptisation)
Question 3: Which of the following is less than zero during adsorption?
- ΔG
- ΔS
- ΔH
- All of these
Answer: D (All of these)
Question 4: The incorrect statement about physical adsorption is
- It lacks specificity
- It is generally reversible
- Porous surfaces are good adsorbent
- Heat of adsorption is quite high
Answer: D (Heat of adsorption is quite high)
Question 5: Fog is an example of colloid system of
- Liquid in gas
- Gas in liquid
- Solid in gas
- Gas in solid
Answer: A (Liquid in gas)
Question 6: Shape selective catalysis is a reaction catalysed by
- Zeolites
- Enzymes
- Platinum
- Ziegler Natta catalyst
Answer: A (Zeolites)
Question 7: The activity of an enzyme becomes ineffective
- At low temperature
- At atmospheric pressure
- At high temperature
- In aqueous medium
Answer: C (At high temperature)
Question 8: A colloidal system in which liquid is dispersed phase and solid is dispersion medium is classified as
- Gel
- Sol
- Emulsion
- Aerosol
Answer: A (Gel)
Question 9: Substances which behave as normal electrolytes in solution at low concentration and exhibit colloidal properties at higher concentration are called
- Lyophilic colloids
- Lyophobic colloids
- Macromolecular colloids
- Associated colloids
Answer: D (Associated colloids)
Question 10: Which of the following examples is correctly matched?
- Butter – gel
- Smoke – emulsion
- Paint – foam
- Milk – aerosol
Answer: A (Butter – gel)
Question 11: The formation of micelles takes place only above
- Critical temperature
- Kraft temperature
- Inversion temperature
- Absolute temperature
Answer: B (Kraft temperature)
Question 12: Soap mixed with water below critical micelle concentration behave as
- Associated colloid
- Macromolecular colloid
- Normal electrolytic solution
- Multimolecular colloid
Answer: C (Normal electrolytic solution)
Question 13: Tyndall effect is not observed in
- Smoke
- Emulsions
- Sugar solution
- Gold sol
Answer: C (Sugar solution)
Question 14: Which of the following is not a method of removing impurities from a colloidal sol?
- Electrodialysis
- Ultrafiltration
- Ultracentrifugation
- Distillation
Answer: D (Distillation)
Question 15: Movement of the dispersion medium under the influence of electric field is known as
- Electrodialysis
- Electrophoresis
- Electro osmosis
- Cataphoresis
Answer: C (Electro osmosis)
Question 16: At CMC, the surface molecules
- Dissociate
- Associate
- Become bigger in size due to adsorption
- Become smaller in size due to decomposition
Answer: B (Associate)
Question 17: The separation of an emulsion into its constituent liquids is known as
- Emulsification
- Protection of colloid
- Coagulation
- Demulsification
Answer: D (demulsification)
Question 18: Which of the following is not an example of an emulsifying agent?
- Proteins
- Gums
- Soaps
- Electrolytes
Answer: D (Electrolytes)
Question 19: What happens when a lyophilic sol is added to a lyophobic sol?
- Lyophilic sol is protected
- Lyophobic sol is protected
- Both the sols are coagulated
- Electrophoresis takes place
Answer: B (Lyophobic sol is protected)
Question 20: The Brownian motion is due to
- Temperature fluctuation within the liquid phase
- Attraction and repulsion between charges on the colloidal particles
- Impact of molecules of the dispersion medium on the colloidal particles
- Convective currents
Answer: C (Impact of molecules of the dispersion medium on the colloidal particles)
Question 21: Which of the following is not characteristics of chemisorption?
- Adsorption is specific
- Heat of adsorption is of the order of 200 KJ mol-1
- Adsorption is irreversible
- Adsorption may be multimolecular layers
Answer: D (Adsorption may be multimolecular layers)
Question 22: Which property of colloid is not dependent on the charge of colloidal particles?
- Coagulation
- Electrophoresis
- Electroosmosis
- Tyndall effect
Answer: D (Tyndall effect)
Question 23: In the adsorption of a gas on solid, Freundlich isotherm is obeyed. The slope of the plot is zero. Thus, the extent of adsorption is
- Directly proportional to the pressure of gas
- Inversely proportional to the pressure of gas
- Independent of the pressure of the gas
- Proportional to the square of the pressure of the gas
Answer:C (Independent of the pressure of the gas)
Question 24: Which of the following can adsorb larger volume of hydrogen gas?
- Finely divided platinum
- Colloidal solution of palladium
- Small pieces of palladium
- A single metal surface of palladium
Answer: B (Colloidal solution of palladium)
[Hint: In colloidal solution particles are suspended and are more dispersed than powdered form]
Question 25: The term ‘sorption’ stands for
- Adsorption
- Absorption
- Both adsorption and absorption
- Desorption
Answer:C (Both adsorption and absorption)
Question 26: Which of the following is not a property for physical adsorption?
- Unilayer adsorption occurs
- Greater the surface area, more the adsorption
- Lower the temperature, more the adsorption
- Higher the pressure, more the adsorption
Answer: A (Unilayer adsorption occurs)
Question 27: The emulsifying agent present in milk that makes it stable is
- Lactose
- Maltose
- Casein
- Lactic bacilli
Answer:C (casein)
Question 28: Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- On prolonged dialysis colloid becomes stable.
- AgNO3 in excess KI forms negative colloid.
- AgNO3 in excess KI forms positive colloid.
- Medicines work best in colloidal form because of greater surface area.
Answer: C (AgNO3 in excess KI forms positive colloid.)
Question 29: Paints and hair creams are respectively
- Sol and emulsion
- Aerosol and foam
- Emulsion and sol
- Foam and gel
Answer: A (Sol and emulsion)
Question 30: The values of colligative properties of colloidal solution are of small order in comparison to those shown by true solutions of same concentration because colligative particles
- Exhibit enormous surface area
- Remain suspended in the dispersion medium
- Form lyophilic colloids
- Are comparatively less in number
Answer: D (Are comparatively less in number)
MCQ of General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Question 1: Which of the following is not an oxide ore?
- Corundum
- Zincite
- Calamine
- Chromite
Answer: C (Calamite)
Question 2: Which one of the following is not a sulphide ore?
- Galena
- Iron pyrites
- Magnetite
- Copper glance
Answer: C (Magnetite)
Question 3: Which of the following ores cannot be concentrated by magnetic separation?
- Haematite
- Malachite
- Magnetite
- Siderite
Answer: B (Malachite)
Question 4: Sulphide ore of zinc/ copper is concentrated by
- Floatation process
- Electromagnetic process
- Gravity separation
- Distillation
Answer: A (floatation process)
Question 5: Which of the following metals is not extracted by leaching?
- Aluminium
- Mercury
- Silver
- Gold
Answer: B (Mercury)
Question 6: Heating pyrites to remove sulphur is called
- Smelting
- Calcination
- Liquation
- Roasting
Answer:D (Roasting)
Question 7: Froth floatation process of concentration is based on the
- Preferential wetting properties with the frothing agent and water
- Difference in specific gravities of gangue and ore particles
- Difference in solubility of gangue and ore particles in frothing agent and water
- Difference in reactivity of gangue and ore particles with water and frothing agent.
Answer: A (Preferential wetting properties with the frothing agent and water)
Question 8: Which of the following metal is extracted using a silica lined convertor ?
- Mg
- Al
- Cu
- Zn
Answer: C (Cu)
Question 9: During the extraction of haematite , limestone is added which acts as
- Flux
- Slag
- Reducing agent
- Gangue
Answer: A (flux)
Question 10: The main difference between cast iron and pig iron is
- Cast iron is purest form of iron while pig iron is impure
- Cast iron has low carbon content (3%) as compared to pig iron (4%) and is extremely hard and brittle
- Pig iron contains many impurities like S, P Si and Mn while cast iron does not contain any impurity and can be casted into any shape
- Cast iron is soft and malleable while pig iron is extremely hard and brittle
Answer: B (Cast iron has low carbon content (3%) as compared to pig iron (4%) and is extremely hard and brittle)
Question 11: In metallurgical process, aluminium acts as
- An oxidising agent
- A reducing agent
- Acidic flux
- Basic flux
Answer: B (A reducing agent )
Question 12: Which of the following metals cannot be obtained by reduction of its metal oxide by aluminium?
- Cr
- Mn
- Fe
- Mg
Answer: D (Mg)
Question 13: Extraction of chlorine from brine is based on
- Reduction
- Displacement
- Oxidation
- Evaporation
Answer: C (Oxidation)
Question 14: In electro-refining of copper, some gold is deposited as
- Cathode mud
- Electrolyte
- Anode mud
- Cathode
Answer: C (Anode mud)
Question 15: In blast furnace iron oxide is reduced by
- Silica
- Carbon monoxide
- Carbon
- Lime stone
Answer: B (Carbon monoxide)
Question 16: Sulphide ores are converted to oxides before reduction. This is explained on the basis of which of the following?
- Sulphides cannot be reduced easily while oxides can be reduced easily
- Sulphides decompose on reduction hence they are first converted into oxides
- Sulphide ores have higher melting points than oxides
- Oxides are more stable than sulphides hence easy to reduce
Answer: A (Sulphides cannot be reduced easily while oxides can be reduced easily)
Question 17: Blister copper is
- Impure copper
- Obtained by self reduction process during bessemerisation
- Both are correct
- None are correct
Answer: C (Both are correct)
Question 18:Which of the following metal is obtained by electrolytic reduction process?
- Fe
- Cu
- Ag
- Al
Answer: D (Al)
Question 19: Which of the following is the purest commercial form of iron?
- Cast iron
- Steel
- Wrought iron
- Pig iron
Answer: C (Wrought iron)
Question 20: Which of the following pairs of metals is purified by van Arkel method?
- Ni and Fe
- Ga and In
- Zr and Ti
- Ag and Au
Answer: C (Zr and Ti )
Question 21: The temperature of the slag zone in the metallurgy of iron using blast furnace is
- 1500 – 1600ºC
- 400 – 700ºC
- 800 – 1000º C
- 1200 – 1500ºC
Answer: C (800 – 1000º C)
Question 22: During smelting, an additional substance is added which combines with impurities to form a fusible mass. The additional substance is called
- Flux
- Slag
- Gangue
- Ore
Answer: A (flux)
Question 23: Mond’s process is used for refining of
- Ni
- Ag
- Sn
- Al
Answer: A (Ni)
Question 24: During extraction of aluminium from bauxite,
- The concentration of ore is done by gravity separation method
- Molten mixture of aluminium oxide, cryolite or fluorspar is electrolysed
- Impure aluminium is refined by liquation
- Molten aluminium is obatined at cathode while fluorine is liberated at anode
Answer: B (Molten mixture of aluminium oxide, cryolite or fluorspar is electrolysed)
Question 25: Chromatography is a useful method for purification of elements which are
- Very reactive
- Available in minute quantities
- Present in abundance
- Highly electropositive
Answer: B (Available in minute quantities)
MCQ of The P Block Elements Class 12
Question 1: Nitrogen is used to fill electric bulbs because
- It is lighter than air
- It makes the bulb to glow
- It does not support combustion
- It is non-toxic
Answer: C (It does not support combustion)
Question 2: Which oxide of nitrogen is obtained on heating ammonium nitrate at 250º C?
- N2O3
- NO2
- NO
- N2O4
Answer: B (NO2)
Question 3: Which of the following factor would favour the formation of ammonia in Haber’s process?
- High pressure
- Low temperature
- High volume
- Low pressure
Answer: A (High pressure)
Question 4: Atomicity of Phosphorous is
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Answer: D (Four)
Question 5: A gas (X) is obtained when copper reacts with dilute HNO3. The gas thus formed reacts with oxygen to give brown fumes of (Y). (Y) when dissolved in water gives an important acid (Z) and the gas(X). X, Y and Z respectively are
- NO ; NO2 ; HNO3
- NO2 ; NO ; HNO3
- N2O ; NO ; HNO2
- NO ; N2O ; HNO3
Answer: A (NO ; NO2 ; HNO3)
Question 6: Group 16 elements have lower first ionisation enthalpy as compared to group 15 elements because
- Half filled p-orbitals in group 15 elements are more stable
- Group 16 elements have smaller size than group 15 elements
- Group 16 elements contain double bond while group 15 elements have triple bond
- Group 16 elements have more number of elements in p-orbitals
Answer: A (Half filled p-orbitals in group 15 elements are more stable)
Question 7: Covalency of oxygen cannot exceed 2 unlike sulphur which can show +4 or +6 because
- Oxygen atom does not have d orbital
- Oxygen atom has two unpaired electron in its valence shell
- Oxygen can form a double bond with another oxygen atom
- Electrons of oxygen atom cannot be promoted to d-orbital due to its small size
Answer: A (Oxygen atom does not have d orbital)
Question 8: Bond angle in H2O (104.5º) is higher than the bond angle of H2S (92.1º) . The difference is due to
- O is diatomic and S is tetra atomic
- Difference in electronegativity of S and O
- Difference in oxidation states of S and O
- Difference in shapes of hybrid orbitals of S and O
Answer: B (Difference in electronegativity of S and O)
Question 9: Which is the correct arrangement of the compounds based on their bond strength?
- HF > HCl > HBr > HI
- HI > HBr > HCl > HF
- HCl > HF > HBr > HI
- HF > HBr > HCl > HI
Answer: A (HF > HCl > HBr > HI)
Question 10: In which of the following, sulphur is present in +5 oxidation state?
- Dithionic acid
- Sulphurous acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Disulphuric acid
Answer: A (Dithionic acid)
Question 11: The correct order of increasing electron affinity of halogens is
- I < Br < Cl
- Br < I < Cl
- Cl < Br < I
- I < Cl < Br
Answer: A (I < Br < Cl)
Question 12: The comparatively high boiling point of hydrogen fluoride is due to
- High reactivity of fluorine
- Small size of hydrogen atom
- Formation of hydrogen bonds
- Small size of fluorine
Answer: C (Formation of hydrogen bonds)
Question 13: When three parts of concenrated HCl and one part of conc. HNO3 is mixed, a compound X is formed. The correct option related to X is
- ‘X’ is known as aqua regia
- ‘X’ is used for dissolving gold
- ‘X’ is used for decomposition of salts of weaker acids
- Both (a) and (b)
Answer: D (Both (a) and (b))
Question 14: What happens when white phosphorous is heated at 473 K under high pressure?
- α- Black phosphorous is formed.
- β- Black phosphorous is formed.
- Red phosphorous is formed.
- No change would be observed.
Answer: B ( β- Black phosphorous is formed )
Question 15: The bleaching of chlorine is due to the liberation of the following
- HOCl
- HCl
- [ O ]
- O2
Answer: C [O]
Question 16: Maximum covalency of nitrogen is…..
- 3
- 5
- 4
- 6
Answer: C (4)
Question 17: Which of the following elements can be involved in pπ—dπ bonding?
- Carbon
- Phosphorous
- Nitrogen
- Boron
Answer: B (Phosphorous)
Question 18: Which of the following elements does not show allotropy?
- Nitrogen
- Bismuth
- Antimony
- Arsenic
Answer: B (Bismuth)
Question 19: Which of the following statement is wrong?
- Single N—N bond is stronger than single P—P bond
- PH3 acts as ligand in the formation of coordination compound with transition elements
- NO2 is paramagnetic in nature
- Covalency of nitrogen in N2O3 is four.
Answer: A ( Single N—N bond is stronger than single P—P bond )
Question 20: Make the correct statement about halogens from the following.
- Electron affinity of halogens is in the order F > Cl > Br > I
- HF is the strongest hydrohalic acid
- F2 has lower bond dissociation energy than Cl2
- All halogens show variable oxidation states.
Answer: C ( F2 has lower bond dissociation energy than Cl2 )
Question 21: If Chlorine is passed through a solution of hydrogen sulphide in water, the solution turns turbid due to the formation of
- Free chlorine
- Free sulphur
- Nascent oxygen
- Nascent hydrogen
Answer: B (Free sulphur )
Question 22: Sulphur molecule is
- Diatomic
- Triatomic
- Tetratomic
- Octa – atomic
Answer: D (Octa – atomic)
Question 23: Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than the individual halogens because
- They are prepared by direct combination of halogens
- X—X’ bond is weaker than X—X or X’—X’ bonds
- They are thermally more stable than halogens
- There is a large difference in their electronegativity
Answer: B ( X—X’ bond is weaker than X—X or X’—X’ bonds)
Question 24: Which of the following is not a use of noble gases?
- Argon is widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs.
- Neon is used in safety devices for protecting electrical bulbs.
- Radon is used in radiotheory of cancer.
- Helium is filled in tubes of cycles and scooter tyres.
Answer: D ( Helium is filled in tubes of cycles and scooter tyres. )
Question 25: A black powder when heated with conc. HCl gives a greenish yellow gas. The gas acts as oxidising and a bleaching agent. When it is passed over slaked lime, a white powder is formed which is a ready source of the greenish yellow gas. The black powder and white powder respectively are
- KClO3 and NaClO3
- MnO2 and Ca(OCl)2
- MnO2 and KClO3
- MnCl4 and COCl2
Answer: B ( MnO2 and Ca(OCl)2 )
Question 26: Nitrogen can form only one chloride with chlorine which is NCl3 whereas P can form PCl3 and PCl5. This is
- Due to absence of d orbitals in nitrogen
- Due to difference in size of N and P
- Due to higher reactivity of P towards Cl than N
- Due to presence of multiple bonding in nitrogen
Answer: A (Due to absence of d orbitals in nitrogen)
Question 27: Covalency of oxygen cannot exceed 2 unlike sulphur which can show +4 or +6 because
- Oxygen atom does not have d orbitals
- Oxygen atom has two unpaired electron in its valence shell
- Oxygen can form a double bond with another oxygen atom
- Electrons of oxygen atom cannot be promoted to d orbitals due to its small size
Answer: A ( Oxygen atom does not have d orbitals )
Question 28: The correct order of increasing affinity of halogens is
- I < Br < Cl
- Br < I < Cl
- Cl < Br < I
- I < Cl < Br
Answer: A (I < Br < Cl)
Question 29: Fluorine is the best oxidising agent because it has
- Highest electron affinity
- Highest reduction potential
- Highest oxidation potential
- Lowest electron affinity
Answer: B (Highest reduction potential)
Question 30: On heating ammonium nitrate and barium azide separately we get
- N2 in both cases
- N2 with ammonium dichromate and NO with barium azide
- N2O with ammonium dichromate and N2 with barium azide
- N2O with ammonium dichromate and NO2 with barium azide
Answer: A ( N2 in both cases )
Question 31: On heating with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO2, white phosphorous gives a gas. Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the gas?
- It is highly poisonous and has smell like rotten fish
- Its solution in water decomposes in the presence of light
- It is more basic than NH3
- It is less basic than NH3
Answer: C (It is more basic than NH3)
Question 32: The comparatively high boiling point of hydrogen fluoride is due to
- High reactivity of fluorine
- Small size of hydrogen atom
- Formation of hydrogen bonds
- Small size of fluorine
Answer: C (Formation of hydrogen bonds)
Question 33: Select the correct statement regarding the properties of dioxygen.
- Dioxygen never reacts with metals
- Dioxygen is diamagnetic in nature
- Combination of dioxygen with other elements is highly exothermic process
- Dioxygen liquefies at 55 K and freezes at 90 K
Answer: C ( Combination of dioxygen with other elements is highly exothermic process )
Question 34: Ammonia is used in detection of Cu2+ ion because
- Aqueous solution of NH3 reacts with Cu2+ ion to form deep blue coloured complex
- NH3 reacts with Cu2+ ion to give blue precipate of CuO
- Aqueous solution of NH3 reacts with Cu2+ ion to form white coloured complex
- NH3 reacts with Cu2+ ion to give green precipitate
Answer: A ( Aqueous solution of NH3 reacts with Cu2+ ion to form deep blue coloured complex )
Question 35: Which of the following is a tetrabasic acid?
- Hypophosphorous acid
- Metaphosphoric acid
- Pyrophosphoric acid
- Orthophosphoric acid
Answer: C (Pyrophosphoric acid)
MCQ of The d- and F- Block Elements
Question 1: Due to lanthanoid contraction which of the following properties is not expected to be similar in the same vertical columns of second and third transition elements?
- Atomic radii
- Ionisation energies
- Magnetic moments
- Lattice energies
Answer: C (Magnetic Moments)
Question 2: Zr and Hf have almost equal atomic and ionic radii because of
- Diagonal relationship
- Lanthanoid contraction
- Actinoid Contraction
- Belonging to the same group
Answer: B ( Lanthanoid Contraction)
Question 3: The second and third row elements of transition metals resemble each other much more than they resemble the first row because of
- Lanthanoid contraction which results in almost same radii of second and third row metals
- Diagonal relationship between second and third row elements
- Similar ionisation enthalpy of second and third row elements
- Similar oxidation states of second and third row metals
Answer: A ( Lanthanoid contraction which results in almost same radii of second and third row metals)
Question 4: The first ionisation energies of the elements of the first transition series (Ti to Cu)
- Increases as the atomic number increases
- Decreases as the atomic number increases
- Do not show any change as the addition of electrons takes place in the inner (n-1)d orbitals
- Increases from Ti to Mn and then decreases from Mn to Cu
Answer: A (Increases as the atomic number increases)
Question 5: The magnetic moment of a divalent ion in aqueous solution with atomic number 25 is
- 5.9 B.M.
- 2.9 B.M.
- 6.9 B.M.
- 9.9 B.M.
Answer: A ( 5.9 B.M.)
Question 6: Which of the following transition metal ion is colourless?
- V 2+
- Cr 3+
- Zn 2+
- Ti 3+
Answer: C (Zn 2+)
Question 7: In which of the following compounds manganese has oxidation number equal to that of iodine in KIO4 ?
- Potassium manganate
- Potassium permanganate
- Dimanganese decarbonyl
- Manganese chloride
Answer: B (Potassium permanganate)
Question 8: Colour of transition metal are due to absorption of some wavelength. This results in
- d-s transition
- s-s transition
- s-d transition
- d-d transition
Answer: D (d-d transition)
Question 9: Interstitial compounds are
- Non – stoichiometric and are ionic in nature
- Non – stoichiometric and are covalent in nature
- Non – stoichiometric and are neither typically ionic nor covalent in nature
- Stoichiometric and are neither ionic nor covalent in nature
Answer: C ( Non – stoichiometric and are neither typically ionic nor covalent in nature)
Question 10: What happens when potassium iodide reacts with acidic solution of potassium dichromate?
- It liberates iodine
- Potassium sulphate is formed
- Chromium sulphate is formed
- All the above products are formed
Answer: D (All the above products are formed)
Question 11: Transition metals make the most efficient catalysts because of their ability to
- Adopt multiple oxidation states and to form complexes
- Form coloured ions
- Show paramagnetism due to unpaired electrons
- Form a large number of oxides
Answer: A (Adopt multiple oxidation states and to form complexes)
Question 12: The most common lanthanoid is
- Lanthanum
- Cerium
- Samarium
- Plutonium
Answer: B (Cerium)
Question 13: Lanthanoid contraction is due to increase in
- Atomic number
- Effective nuclear charge
- Atomic radius
- Valence electrons
Answer: B (Effective nuclear charge)
Question 14: The common oxidation state shown by Europium in their compounds is
- +1
- +3
- +5
- +6
Answer: B (+3)
Question 15: Lanthanides and actinides resemble in
- Electronic configuration
- Oxidation state
- Ionisation energy
- Formation of complexes
Answer: A (Electronic Configuration)
Question 16: Interstitial compounds are formed when small atoms are trapped inside the crystal lattice of metals. Which of the following is not the characteristic property of interstitial compounds?
- They have high melting points in comparison to pure metals.
- They are very hard
- They retain metallic conductivity
- They are chemically very reactive
Answer: D (They are chemically inert)
Question 17: The trend of basicity of lanthanoid hydroxides
- Increases across the lanthanoid series
- Decreases across the lanthanoid deries
- First increases and then decreases
- First decreases and then increases
Answer: B (Decreases along the lanthanoid series)
Question 18: Which of the following statement concerning lanthanide elements is false?
- All lanthanides are highly dense metals.
- Most characteristic oxidation state of lanthanide elements is +3
- Lanthanides are separated from one another by ion exchange method.
- Ionic radii of trivalent lanthanides steadily increases with increase in the atomic number.
Answer: D ( Ionic radii of trivalent lanthanides steadily increases with increase in the atomic number)
Question 19: Which of the following lanthanide ion is paramagnetic?
- Ce 4+
- Yb 2+
- Lu 3+
- Eu 2+
Answer: D (Eu 2+ )
Question 20: Which of the following statements is not correct about magnetic behaviour of substances ?
- Diamagnetic substances are repelled by an applied magnetic field
- Paramagnetic substances are attracted by an applied magnetic field
- Magnetic moment of n unpaired electrons is given by μ = √ n (n-2)
- Magnetic moment increases as the number of unpaired electrons increases
Answer: C ( Magnetic moment of n unpaired electrons is given by μ = √ n (n-2) )
MCQ of Coordination Compounds
Question 1: Which of the following ligands form a chelate?
- Acetate
- Oxalate
- Cyanide
- Ammonia
Answer: B (Oxalate)
Question 2: According to Werner’s theory of coordination compounds
- Primary valency is ionisable
- Secondary valency is ionisable
- Primary and secondary valencies are ionisable
- Neither primary nor secondary valency is ionisable
Answer: A (Primary valency is ionisable)
Question 3: Which of the following rules is not correct regarding IUPAC nomenclature of complex ion?
- Cation is named first and then anion.
- In coordination sphere, the ligands are named alphabetically.
- Positively charged ligands have suffix ‘ate’.
- More than one ligand of a particular type are indicated by using di, tri, tetra etc.
Answer: C ( Positively charged ligands have suffix ‘ate’ )
Question 4: The name of the compound [Co (NH3)5 NO2] Cl2 will be
- pentaamminonitrocobalt (II) chloride
- pentaamminenitrochloridecobaltate(III)
- pentaamminenitrocobalt(III) chloride
- pentanitrosoamminechlorocobaltate(III)
Answer: C ( pentaamminenitrocobalt(III) chloride )
Question 5: Identify the statement which is not correct?
- Coordination compound are mainly known for transition metals.
- Coordination number and oxidation state of a metal are same.
- A ligand donates at least one electron pair to the metal atom to form a bond.
- [Co(NH3)4 Cl2]+ is a heteroleptic complex.
Answer: B ( Coordination number and oxidation state of a metal are same.)
Question 6: CrCl3.6H2O exists in different isomeric forms which shows different colours like violet and green. This is due to
- Ionisation isomerism
- Coordination isomerism
- Optical isomerism
- Hydrate isomerism
Answer: D (Hydrate isomerism)
Question 7: Low spin tetrahedral complexes are not formed because
- For tetrahedral complexes, the CFSE is lower than pairing energy
- For tetrahedral complexes, the CFSE is higher than pairing energy
- Electrons do not go to eg in case of tetrahedral complexes
- Tetrahedral complexes are formed by weak ligands only.
Answer: A ( For tetrahedral complexes, the CFSE is lower than pairing energy )
Question 8: [Fe(CN)6]4- and [Fe(H2O)6]2+ show different colours in dilute solution because
- CN¯ is a strong field ligand and H2O is a weak field ligand hence magnitude of CFSE is different
- Both CN¯ and H2O adsorb same wavelength of energy
- Complexes of weak field ligand are generally colourless
- The sizes of CN¯ and H2O are different hence their colours are also different
Answer: A ( CN¯ is a strong field ligand and H2O is a weak field ligand hence magnitude of CFSE is different )
Question 9: Which of the following will form an octahedral complex?
- d4 (low spin)
- d8 (high spin)
- d6 (low spin)
- None of these
Answer: C ( d6 (low spin) )
Question 10: An example of ambidentate ligand is
- Ammine
- Aqua
- Oxalato
- Thiacyanato
Answer: D (Thiacyanato)
Question 11: How many ions are produced from [Co (NH3)6] Cl3 in the solution?
- 6
- 4
- 3
- 2
Answer: B (4)
Question 12: The oxidation number of [Co(NH3)(NO2)3] is
- +3
- 0
- -3
- +6
Answer: A (+3)
Question 13: The geometry possessed by [Ni(CO)4] is
- Tetrahedral
- Square planar
- Linear
- Octahedral
Answer: A (Tetrahedral)
Question 14: A substance appears coloured because
- It absorbs light at specific wavelength in the visible part and reflects rest of the wavelengths
- Ligands absorb different wavelengths of light which give colour to the complex
- It absorbs white light and shows different colours at different wavelength
- It is diamagnetic in nature
Answer: A ( It absorbs light at specific wavelength in the visible part and reflects rest of the wavelengths )
Question 15:The complex ion which has no d electrons in the central metal atom is
- [MnO4]–
- [Co(NH3)6]3+
- [Fe(CN)6]3-
- [Cr(H2O)6]3+
Answer: A ( [MnO4]– )
Question 16: Which of the following is correct?
- Valence bond theory explains the colour of coordination compounds
- [NiCl4]2- is diamagnetic in nature.
- Ambident ligands can show linkage isomerism.
- A bidentate ligand can have four coordination sites.
Answer: C (Ambident ligands can show linkage isomerism)
Question 17: Which of the following is a tridentate ligand?
- EDTA 4-
- (COO)2 2-
- Dien
- NO2‾
Answer: C ( Dien)
Question 18: Which of the following will not show chelation?
- EDTA
- DMG
- Ethane-1,2-diamine
- SCN¯
Answer: D (SCN‾)
Question 19: The correct structure of Fe(CO)5 is
- Octahedral
- Tetrahedral
- Square pyramidal
- Trigonal bipyramidal
Answer: D (Trigonal bipyramidal)
Question 20: State the true statement from the following metal carbonyls
- π back bonding strengthens M—C bond order as well as CO bond order
- π back bonding weakens M—C bond order as well as CO bond order
- π back bonding weakens M—C bond order but strengthens CO bond order
- π back bonding strengthens M—C bond order and weakens CO bond order.
Answer: D ( π back bonding strengthens M—C bond order and weakens CO bond order )
MCQ of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Question 1: Which of the following is a primary halide?
- iso-Propyl iodide
- sec-Butyl iodide
- tert-Butyl iodide
- neo-Hexyl chloride
Answer: D (neo-Hexyl halide)
Question 2: The main difference in C—X bond of a haloalkanes and haloarenes is
- C—X bond in haloalkane is shorter than haloarenes.
- In haloalkane the C attached to halogen in C—X bond is sp3 hybridised while in haloarenes it is sp2 hybridised
- C—X bond in haloarenes acquires a double character due to higher electronegativity of X than haloalkanes.
- Haloalkanes are less reactive than haloarenes due to difficulty in C—X cleavage in haloalkanes.
Answer: B ( In haloalkane the C attached to halogen in C—X bond is sp3 hybridised while in haloarenes it is sp2 hybridised )
Question 3: Which of the following can yield only monochlorinated product upon free radical chlorination?
- 2,2-Dimethylpropane
- 2-Methylpropane
- 2-Methylbutane
- n-Butane
Answer: A (2,2-Dimethylbutane)
Question 4: Bromination of methane in presence of sunlight is a
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Free radical substitution
- Electrophic substitution
- Nucleophilic addition
Answer: B (Free radical substitution)
Question 5: Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by SN2 mechanism because
- The carbocation formed is unstable.
- There is steric hindrance
- There is inductive effect
- The rate of reaction is faster in SN2 mechanism
Answer: B (There is steric hindrance)
Question 6: Which of the following haloalkanes is most reactive?
- 1-Chloropropane
- 1-Bromopropane
- 2-Chloropropane
- 2-Bromopropane
Answer: D (2-Bromopropane)
Question 7: Which of the following haloalkanes reacts with aqueous KOH most easily?
- 1-Bromobutane
- 2-Bromobutane
- 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane
- 2-Chlorobutane
Answer: C (2-Bromo-2-methylpropane)
Question 8: 2-Bromo-3,3-dimethylbutane on reaction with aqueous KOH yields X as the major product. X is
- 2,3,3-trimethylpropan-1-ol
- 2,2-dimethylbutan-3-ol
- 2,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol
- 2,2-dimethylpropan-2-ol
Answer: C (2,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol)
Question 9: A mixture of 1-chloropropane and 2-chloropropane when treated with alcoholic KOH gives
- prop-1-ene
- prop-2-ene
- A mixture of prop-1-ene and prop-2-ene
- propanol
Answer: A (prop-1-ene)
Question 10: Chlorobenzene on treatment with on treatment with sodium in dry ether gives diphenyl. The name of the reaction is
- Fittig reaction
- Wurtz Fittig reaction
- Sandmeyer reaction
- Gattermann reaction
Answer: A (Fittig Reaction )
Question 11: Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions as compared to alkyl halides due to
- Formation of less stable carboniym ion in aryl halides
- Resonance stabilisation in aryl halides
- Presence of double bonds in alkyl halides
- Inductive effect in aryl halides
Answer: B (Resonance stabilisation in aryl halides)
Question 12: Which of the following is an example of vic-dihalide?
- Dichloromethane
- 1,2-Dichloroethane
- Ethylidene chloride
- Allyl chloride
Answer: B (1,2-Dichloroethane)
Question 13: An organic halogen which is used as refrigerant in refrigerators and air conditioners is
- BHC
- CCl4
- Freon
- CHCl3
Answer: C (Freon)
Question 14: When ethyl iodide is heated with dry silver oxide, it forms
- Ethyl alcohol
- Diethyl ether
- Silver ethoxide
- Ethyl methyl ether
Answer: B (Diethyl ether)
Question 15: iso-propyl bromide on Wurtz reaction gives
- Hexane
- Propane
- 2,3-Dimethylbutane
- Neo-hexane
Answer: C (2,3-dimethylbutane)
Question 16: Which of the following compound will have highest melting point?
- Chlorobenzene
- o-Dichlorobenzene
- m-Dichlorobenzene
- p-Dichlorobenzene
Answer: D (p-Dichlorobenzene)
Question 18: Alkyl halides are immiscible in water though they are polar because
- They react with water to give alcohols
- They cannot form hydrogen bonds with water
- C—X bond cannot be broken easily
- They are stable compounds and are not reactive.
Answer: B (They cannot form hydrogen bonds with water)
Question 19: The alkyl halide is converted into an alcohol by
- Elimination
- Dehydrohalogenation
- Addition
- Substitution
Answer: D (Substitution)
Question 20: In SN2 reactions the sequence of bond breaking and bond formation is as follows
- Bond breaking is followed by formation.
- Bond formation is followed by breaking.
- Bond breaking and formation occur simultaneously.
- Bond breaking and formation take place randomly
Answer: C (Bond breaking and formation occur simultaneously)
Question 21: Which of the following posses highest melting point?
- Chlorobenzene
- o-Dichlorobenzene
- m-Dichlorobenzene
- p-Dichlorobenzene
Answer: D (p- Dichlorobenzene)
Question 22: Which of the following event does not occur during SN2 reaction mechanism ?
- Back side attack of nucleophile
- Formation of carbonium ion
- One step continuous process
- 100 % inversion of configuration
Answer: B (Formation of carbonium ion)
Question 23: In which of the following case; halogen exchange reaction will occur ?
- R — I + NaCl
- R — F + KCl
- R — Cl + NaI
- CH3—F + AgBr
Answer: C ( R — Cl + NaI )
Question 24: Ethyne can be formed from which of the following reactant in one step
- Ethanol
- Ethanal
- Chloroform
- Ethyl bromide
Answer: C (Chloroform)
Question 25: When Chlorobenzene is treated with sodium in presence of dry ether , it gives diphenyl. This reaction is commonly known as
- Fittig Reaction
- Wurtz Fittig Reaction
- Sandmeyer reaction
- Wurtz Reaction
Answer: A (Fittig reaction)
Question 26: Bromoalkane can easily be prepared by refluxing the silver salt of fatty acid with bromine in carbon tetrachloride. This reaction is commonly known as
- Birnbaum Simonini reaction
- Borodine Hunsdiecker reaction
- Swarts reaction
- None of the above
Answer: B (Borodine Hunsdiecker reaction)
Question 27: Which of the following statement regarding boiling point of Haloalkane is incorrect?
- For the same alkyl group, boiling point decreases in the order : RI > RBr > RCl > RF
- Boiling point of chloro, bromo and iodo compounds increases as number of halogen atom increases.
- For same halogen atom boiling point increases with increase in size of the alkyl group.
- For same halogen atom boiling point decreases with increase in size of the alkyl group.
Answer: D ( For same halogen atom boiling point decreases with increase in size of the alkyl group )
Question 28: Haloalkanes on treatment with AgOH underogoes hydrolysis to yield
- Haloarenes
- Alcohols
- Aldehyde
- Carboxylic Acids
Answer: B (Alcohols)
Question 29: Substitution nucleophilic unimolecular follows ….. order kinetics.
- Second
- Third
- First
- None of the above
Answer: C (First)
Question 30: Which of the following carbocation is most reactive towards SN1 reaction ?
- Tertiary
- Secondary
- Primary
- Methyl
Answer: A (Tertiary)
MCQ of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Question 1: There is a large difference in the boiling points of butanal and butan-1-ol due to
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in butan-1-ol
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in butanal
- Higher molecular mass of butan-1-ol
- Resonance shown by butanal
Answer: A ( Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in butan-1-ol )
Question 2: The oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by chromyl chloride is called
- Etard reaction
- Riemer Tiemann reaction
- Wurtz reaction
- Cannizzaro reaction
Answer: A (Etard reaction)
Question 3: Ozonolysis of an organic compound gives benzaldehyde as one of the products. This confirms the presence of
- Two ethylenic double bond
- A vinyl group
- An isopropyl group
- An acetylenic triple bond
Answer: B (A Vinyl group)
Question 4: The addition of HCN to carbonyl compound is an example of
- Nucleophilic addition
- Electrophilic addition
- Free radical addition
- Elimination addition
Answer: A (Nucleophilic addition)
Question 5: Aldehydes other than formaldehyde react with grignard reagent to give addition product which on hydrolysis give
- Tertiary alcohols
- Secondary alcohols
- Primary alcohols
- Carboxylic acids
Answer: B (Secondary alcohols)
Question 6: Hydrocarbons are formed when aldehydes and ketones are reacted with amalgamated zinc and conc. HCl . This reaction is called
- Cannizaro reaction
- Clemmensen reaction
- Rosenmund reduction
- Wolff Kishner reduction
Answer: B ( Clemmensen reaction)
Question 7: Which of the following statement is not correct?
- Aldehydes and ketones are functional isomers
- Formaldehyde reacts with ammonia to form hexamethylenetetramine.
- LiAlH4 convert ketones into sec-alcohols.
- Ethanal and propanal give positive iodoform test
Answer: D ( Ethanal and propanal give positive iodoform test )
Question 8: Which of the following can be used to distinguish aldehydes and ketones?
- Fehling’s solution
- H2SO4 solution
- NaHSO3
- NH3
Answer: A (Fehling’s solution)
Question 9: When propanol reacts with 2-methylpropanal in presence of NaOH, four different products are formed. This reaction is known as
- Aldol condensation
- Cross aldol condensation
- Cannizzaro reaction
- HVZ Condensation
Answer: B (Cross aldol condensation)
Question 10: Carboxylic acids dimerise due to
- High molecular weighet
- Coordinate bonding
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding
- Covalent bonding
Answer: C (Intermolecular hydrogen bonding)
Question 11: Which of the following carboxylic acids is highly insoluble in water?
- Propanoic acid
- Butanoic acid
- Pentanoic acid
- Decanoic acid
Answer: D (Decanoic acid)
Question 12: —OH group present in alcohols is neutral while it is acidic in carboxylic acid because
- In carboxylic acid —OH group is attached to electron withdrawing carbonyl group
- In alcohols —OH group is attached to alkyl group which is electron withdrawing
- Carboxylic group is an electron releasing group
- Alcoholic group is an electron withdrawing group
Answer: A ( In carboxylic acid —OH group is attached to electron withdrawing carbonyl group )
Question 13: What happens when carboxylic acid is treated with lithium aluminium hydride?
- Aldehyde is formed
- Primary alcohol is formed
- Ketone is formed
- Grignard reagent is formed
Answer: B (Primary alcohol is formed)
Question 14: The reagent which does not react with both acetone and benzaldehyde is
- Sodium hydrogensulphite
- Phenyl hydrazine
- Fehling’s solution
- Grignard reagent
Answer: C (Fehling’s solution)
Question 15:Which of the following will not undergo HVZ reaction?
- Propanoic acid
- Ethanoic acid
- 2-Methylpropanoic acid
- 2,2-Dimethylpropanoic acid
Answer: D (2,2-Dimethylpropanoic acid)
Question 16: Choose the correct statement regarding the physical properties of chemical compounds.
- All aldehydes are insoluble in benzene
- Higher aldehydes are more fragrant
- n-Butane has more boiling point than acetone.
- Methanal and propanone are immiscible water in all proportions
Answer: B (Higher aldehydes are more fragrant)
Question 17: Methyl ketones are characterised through
- Tollens’ reagent
- Iodoform test
- Schiff’s reagent
- Fehling’s solution
Answer: B (Iodoform test)
Question 18: Which of the following compound will give butanone on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 solution?
- Butan-1-ol
- Butan-2-ol
- Both of these
- None of these
Answer: B (Butan-2-ol)
Question 19: Which of the following statement is correct regarding formic acid?
- It is a reducing agent.
- It is a weaker acid than acetic acid
- It is an oxidising agent.
- When its calcium salt is heated, it forms acetone.
Answer: A (It is a reducing agent)
Question 20: Which of the following will not give aldol condensation?
- Phenyl acetaldehyde
- 2-Methylpentanal
- Benzaldehyde
- 1-Phenylpropanone
Answer: C (Benzaldehyde)
MCQ of Amines
Question 1: Reduction of aromatic nitro compounds using Sn and HCl gives
- Aromatic primary amines
- Aromatic secondary amines
- Aromatic tertiary amines
- Aromatic amides
Answer: A ( Aromatic primary amines )
Question 2: Amine that cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is
- Aniline
- Benzyl amine
- Methyl amine
- Iso-butylamine
Answer: A (Aniline)
Question 3: Amides can be converted into amines by a reaction named after
- Hoffmann
- Claisen
- Perkin
- Kekule
Answer: A (Hoffmann)
Question 4: The most convenient method to prepare an amine containing one carbon atom less is
- Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
- Reductive amination of aldehydes
- Hoffmann bromamide reduction
- Reduction of isonitriles
Answer: C (Hoffmann bromamide reduction)
Question 5: Which of the following test is suitable to differentiate between aniline and benzylamine?
- Aniline gives dye test on diazotisation and reaction with β-napthol while benzylamine gives alcohol
- Benzylamine gives green dye with β-napthol after diazotisation while aniline gives orange dye.
- Aniline gives carbylamine reaction while benzylamine does not.
- Benzylamine gives carbylamine reaction while aniline does not.
Answer: A ( Aniline gives dye test on diazotisation and reaction with β-napthol while benzylamine gives alcohol )
Question 6: The coupling reaction of aryldiazonium chloride with aniline are carried out in
- Strongly acidic medium
- Strongly basic medium
- Mild basic medium
- Mild acidic medium
Answer: D (Mild acidic medium)
Question 9: When a primary amine reacts with chloroform and ethanolic KOH , then the product formed is
- Isocyanide
- Aldehyde
- Cyanide
- Alcohol
Answer: A (Isocyanide)
Question 10: Which of the following compounds will not undergo azo coupling reaction with benzene diazonium chloride?
- Aniline
- Phenol
- Anisole
- Nitrobenzene
Answer: D (Nitrobenzene)
Question 11: Primary, secondary and amines may be separated by using
- Iodoform
- Diethyloxalate
- Benzenesulphonyl chloride
- Acetyl chloride
Answer: C (Benzenesulphonyl chloride)
Question 12: Benzenediaonium chloride cannot be stored and is used immediately after its preparation because
- It slowly evaporates on storage
- It is very unstable and dissociates to give nitrogen
- It gets oxidised in air hence cannot be stored
- It reacts with all the containers in which it is stored
Answer: B (It is very unstable and dissociates to give nitrogen)
Question 13: Benzenediazonium chloride on reaction with phenol in weakly basic medium gives
- diphenyl ether
- p-hydroxyazobenzene
- chlorobenzene
- benzene
Answer: B (p-hydroxyazobenzene)
Question 14: Tertiary amines have lowest boiling points amongst isomeric amines because
- They have highest molecular mass
- They do not form hydrogen bonds
- They are more polar in nature
- They are most basic in nature
Answer: B (They do not form hydrogen bonds)
Question 15: Primary and secondary amines are distinguished by
- Br2/KOH
- HClO
- HNO2
- NH3
Answer: C(HNO2)
Question 16: Basic strength of different alkyl amines depends upon
- +I effect
- Steric effect
- Solvation effect
- All of these
Answer: D (All of these)
Question 17: Which of the following option regarding the property of benzenediazonium fluoroborate?
- It is water soluble at room temperature.
- It is water insoluble and stable at room temperature.
- It is a coloured solid.
- None of these
Answer: B ( It is water insoluble and stable at room temperature )
Question 18: Acid anhydride on reaction with primary amines give
- Amide
- Imide
- Secondary amine
- Imine
Answer: A (Amide)
Question 19: Which of the following orders is true regarding the basic nature of –NH2 group ?
- o-Toluidine > Aniline > o-Nitroaniline
- o-Toluidine < Aniline > o-Nitroaniline
- o-Toluidine < Aniline < o-Nitroaniline
- o-Toluidine > Aniline < o-Nitroaniline
Answer: B ( o-Toluidine < Aniline > o-Nitroaniline )
Question 20: When aniline is heated with conc. H2SO4 at 455 – 475 K, it forms
- Aniline hydrogensulphate
- Sulphanilic acid
- Amino benzene sulphonic acid
- Benzenesulphonic acid
Answer: B (Sulphanilic acid)
MCQ of Biomolecules
Question 1: Cellulose is a
- Hexapolysaccharide
- Pentapolysaccharide
- Tripolysaccharide
- None of these
Answer: D (None of these)
Question 2: Which of the following is an example of aldopentose?
- D-Ribose
- Glyceraldehyde
- Fructose
- Erythrose
Answer: A (D-Ribose)
Question 3: Glycosidic linkage is an
- Amide linkage
- Ester linkage
- Ether linkage
- Acetyl linkage
Answer: C (Ether linkage)
Question 4: Which of the following statement is not true?
- Glucose and fructose both are monosaccharides
- The natural glucose and fructose are D-forms.
- The solution having equal molecules of D-glucose and D-fructose is termed as invert sugar.
- Aldohexoses exist in 26 optical forms.
Answer: D ( Aldohexoses exist in 26 optical forms)
Question 5: How many C atoms are there in a pyranose ring?
- 3
- 5
- 6
- 7
Answer: B (5)
Question 6: Starch is composed of two polysaccharides which are
- Amyloceptin and Glycogen
- Amylose and Glycogen
- Amylose and Amyloceptin
- Cellulose and Glycogen
Answer: C (Amylose and Amyloceptin)
Question 7: Which one of the amino acids can be synthesised in the body?
- Alanine
- Lysine
- Valine
- Histidine
Answer: A (Alanine)
Question 8: The number of amino acids required for protein synthesis is
- 20
- 25
- 10
- 100
Answer: A (20)
Question 9: In Fibrous proteins, the polypeptide chains are held together by
- Van der Waals forces
- Electrostatic forces of attraction
- Hydrogen bonds
- Covalent bonds
Answer: C (Hydrogen bonds)
Question 10: Primary structure of protein is
- Sequence in which α amino acids are linked to one another
- Sequence in which amino acids of one polypeptide chain are joined to another chain
- The folding patterns of polypeptide chains
- The pattern in which the polypeptide chains are arranged
Answer: A (Sequence in which α amino acids are linked to one another)
Question 11: Secondary structure of protein refers to
- Sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chains
- Bonds between alternate polypeptide chains
- Folding patterns of polypeptide chain
- Bonding between NH3+ and COO¯ of two peptides.
Answer: C (Folding pattern of polypeptide chain)
Question 12: Denaturation of protein leads to loss of its biological activity by
- Formation of amino acids
- Loss of primary structure
- Loss of both primary and secondary structures
- Loss of both secondary and tertiary structures
Answer: D (Loss of both secondary and tertiary structures)
Question 13: On boiling the egg, what structural changes are taking place in the egg white?
- The colour of the egg changes from colourless to white
- 2º and 3º structures are destroyed but primary structure remain intact.
- 1º, 2º and 3º structures of egg are destroyed.
- A reversible change take place which can be reversed by decreasing the temperature.
Answer: B (2º and 3º structures are destroyed but primary structure remain intact)
Question 14: Which of the following bases is not present in DNA ?
- Adenine
- Uracil
- Thymine
- Cytosine
Answer: B (Uracil)
Question 15: The two main differences between RNA and DNA are
- Ribose sugar and thymine in RNA
- Deoxyribose sugar and uracil in DNA
- Ribose sugar and uracil in RNA
- Deoxyribose sugar and guanine in DNA
Answer: C (Ribose sugar and uracil in RNA)
Question 16: In a protein molecule various amino acids are linked together by
- Peptide bond
- Dative bond
- α-Glycosidic bond
- β-Glycosidic bond
Answer: A (Peptide bond)
Question 18: Which of the following statement is not true about RNA?
- It is present in the nucleus of the cell.
- It has always double stranded α- helix structure.
- It controls the synthesis of protein
- It usually does not replicate
Answer: B ( It has always double stranded α- helix structure )
Question 19: Which of the following reaction of glucose can be explained only by its cyclic structure?
- Glucose forms pentaacetate
- Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form an oxime
- Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine
- Glucose is oxidised by nitric acid to gluconic acid
Answer: C ( Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine )
Question 20: A unit in nucleic acid which contains ‘base sugar phosphate’ unit is called
- Nucleotide
- Nucleoside
- Phosphotide
- Polypeptide
Answer: A (Nucleotide)
MCQ of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Question 1: Tertiary butyl alcohol can be prepared by the reaction of
- Acetaldehyde and ethyl magnesium iodide
- Acetone and methyl magnesium iodide
- Formaldehyde and propyl magnesium iodide
- Butanone and methyl magnesium iodide
Answer: B (Acetone and methyl magnesium iodide)
Question 2: Propanone on reaction with alkyl magnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis will produce
- Primary alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid
Answer: C (Tertiary alcohol)
Question 3: Which of the following is not a characteristic of alcohol?
- They are lighter than water.
- Their boiling point raise fairly uniformly with rising molecular weight.
- Lower members are insoluble in water and organic solvents but the solubility regularly increases with molecular mass.
- Lower members have a pleasant smell and burning taste , higher members are colourless and tasteless.
Answer: C ( Lower members are insoluble in water and organic solvents but the solubility regularly increases with molecular mass )
Question 4: Order of esterification of alcohols is
- 3º > 1º > 2º
- 2º > 3º > 1º
- 1º > 2º > 3º
- None of these
Answer: C ( 1º > 2º > 3º )
Question 5: Vapours of alcohol X when passed over hot reduced copper, produce an alkene, the alcohol is
- Primary alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
- Dihydric alcohol
Answer: C (Tertiary alcohol)
Question 6: Phenol when treated with excess of bromine water gives a white precipitate of
- 2,4,6-tribromophenol
- o-bromophenol
- p-bromophenol
- bromobenzene
Answer: A (2,4,6-tribromophenol)
Question 7: Conversion of ethyl alcohol into acetaldehyde is an example of
- Hydrolysis
- Oxidation
- Reduction
- Molecular rearrangement
Answer: B (Oxidation)
Question 8: The reaction between phenol and chloroform in presence of aqueous NaOH is
- Nucleophilic substitution reaction
- Electrophilic addition reaction
- Electrophilic substitution reaction
- Nucleophilic addition reaction
Answer: C ( Electrophilic substitution reaction )
Question 9: Which of the following statement is correct?
- The reaction of methyl magnesium iodide with acetone followed by hydrolysis gives secondary butanol
- Primary alcohols are dehydrated easily than secondary and tertiary alcohols
- Tertiary alcohol is more acidic than primary alcohol
- Tertiary butyl alcohol gives turbidity fastest with Lucas reagent.
Answer: D ( Tertiary butyl alcohol gives turbidity fastest with Lucas reagent)
Question 10: Ethers have lower boiling points than corresponding isomeric alcohol because of
- Hydrogen bonding in alcohols that is absent in ethers due to lower polarity
- Hydrogen bonding in ethers due to high polarity
- Insolubility of ethers in water due to less polarity
- Inertness of ethers as compared to alcohols
Answer: A ( Hydrogen bonding in alcohols that is absent in ethers due to lower polarity )
Question 11: Phenol is less acidic than
- Ethanol
- o-Nitrophenol
- o-Methylphenol
- o-Methoxyphenol
Answer: B (o-nitrophenol)
Question 12: Which of the following is most acidic?
- Benzyl alcohol
- Cyclohexanol
- Phenol
- m-Chlorophenol
Answer: D (m-Chlorophenol)
Question 13: Boiling point of ethyl alcohol is greater than ether due to
- Van der Waals forces
- London forces
- Polarity
- Hydrogen bonding
Answer: D (Hydrogen bonding)
Question 14: An ether is more volatile than alcohol having the same molecular mass. This is due to
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in alcohols
- Dipolar character of ethers
- Alcohol having resonance structures
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in ethers
Answer: A (Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in alcohols)
Question 15: When ethanol is heated with HI and red phosphorous, it gives
- Ethyl iodide
- Ethane
- Ethylene
- Ether
Answer: B (Ethane)
Question 16: The reaction of Lucas reagent is fast with
- Ethanol
- Methanol
- 2-Propanol
- 2-Methyl-2-propanol
Answer: D (2-Methyl-2-propanol)
Question 17: The process of converting alkyl halides into alcohols involves
- Addition reaction
- Substitution reaction
- Dehydrohalogenation reaction
- Rearrangement reaction
Answer: B (Substitution reaction)
Question 18: Picric acid is a yellow coloured compound. Its chemical name is
- m-nitrobenzoic acid
- 2,4,6-trinitrophenol
- 2,4,6-tribromophenol
- p-nitrophenol
Answer: B (2,4,6-trinitrophenol)
Question 19: The C—O—H bond angles in alcohols is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle whereas the C—O—C bond angle in ether is slightly greater because
- Of repulsion between the two bulky R groups
- O atom in both alcohols and ethers is sp3- hybridised
- Lone pair-lone pair repulsion is greater than bond pair – bond pair repulsion
- None of these
Answer: A (Of repulsion between the two bulky R groups)
Question 20: The best method to prepare 3-methylbutan-2-ol from 3-methylbut-1-ene is
- Addition of water in dilute H2SO4
- Addition of HCl followed by reaction with dil. NaOH
- Hydroboration oxidation reaction
- Riemer Tiemann reaction
Answer: A(Addition of water in dilute H2SO4 )
MCQ of Polymers
Question 1: Glycogen is a naturally occurring polymer stored in animals is a
- Monosaccharide
- Disaccharide
- Trisaccharide
- Polysaccharide
Answer: D (Polysaccharide)
Question 2: Which of the following is not a characteristic of thermosetting polymers?
- Linear or slightly branched long chain polymers
- Heavily branced and cross linked polymers
- Become infusible on moulding
- Cannot be remoulded or reused on heating
Answer: A (Linear or slightly branched long chain polymers)
Question 3: Bakelite is an example of
- Elastomer
- Fibre
- Thermoplastic
- Thermosetting
Answer: D (Thermosetting)
Question 4: Which factor imparts the crystalline nature to a polymer like nylon?
- Strong intermolecular forces like hydrogen bonding between chains
- van der Waals’ forces between the polymeric chains
- Close packing of chains due to ionic bonding between the chains
- Three dimensional network of chains
Answer: A ( Strong intermolecular forces like hydrogen bonding between chains )
Question 5: High density polythene is obtained by
- Polymerisation of ethene in a hydrocarbon solvent in the presence of Ziegler Natta catalyst
- Polymerisation of ethene under high pressure and temperature
- Free radical polymerisation of ethene at low temperature in presence of peroxides
- Polymerisation of ethene in presence of carbon tetrachloride
Answer: A (Polymerisation of ethene in a hydrocarbon solvent in the presence of Ziegler Natta catalyst )
Question 6: Which of the following is not true about high density polythene?
- Tough
- Hard
- Inert
- Highly branched
Answer: D (Highly branched)
Question 7: Polymer which has amide linkage is
- Nylon-6,6
- Terylene
- Teflon
- Bakelite
Answer: A (Nylon-6,6)
Question 8: Formation of nylons and polyesters are called step growth polymerisation because
- The polymers are formed by adding a monomer step by step
- The polymers are formed by condensation and monomers are joined by loss of simple molecules like water
- The monomers used for condensation are unsaturated molecules
- The polymers are formed by addition of large number of free radicals formed by monomers
Answer: B ( The polymers are formed by condensation and monomers are joined by loss of simple molecules like water )
Question 9: The monomers of biodegradable polymer, nylon 2-nylon 6 are
- Glycine + adipic acid
- Glycol + phthalic acid
- Phenol + urea
- Glycine + amino caproic acid
Answer: D (Glycine + amino caproic acid)
Question 10: Which of the following statements is not true about low density polythene?
- Tough
- Hard
- Poor conductor of electricity
- Highly branched structure
Answer: B (Hard)
Question 11: Which of the following is not an example of rubber?
- Polychloroprene
- Buna-N
- Butadiene- styrene copolymer
- Polyacrylonitrile
Answer: D (Polyacrylonitrile)
Question 12: The difference in the densities of low density (LDP) and high density polymers (HDP) is due to the fact that
- LDP are highly branched structures while HDP consists of closely packed linear molecules
- LDP are linear chains while HDP are branched chains of polythene
- Both LDP and HDP are unbranched linear chains with different lengths
- At high temperature, the density of polymer is reduced
Answer: A ( LDP are highly branched structures while HDP consists of closely packed linear molecules )
Question 13: Teflon and neoprene are the examples of
- Copolymers
- Monomers
- Homopolymers
- Condensation polymers
Answer: C (Homopolymers)
Question 14: Arrange the following polymer in an increasing order of intermolecular forces: Fibre, plastic. elastomer
- Elastomer < Fibre < Plastic
- Elastomer < Plastic < Fibre
- Plastic < Elastomer < Fibre
- Fibre < Elastomer < Plastic
Answer: B (Elastomer < Plastic < Fibre )
Question 15: The S in buna-S refers to
- Sulphur
- Styrene
- Sodium
- Salicylate
Answer: B (Styrene)
Question 16: Terylene is condensation polymer of ethylene glycol and
- Benzoic acid
- Phthalic acid
- Terephthalic acid
- Salicylic acid
Answer: C (Terephthalic acid)
Question 17: Which of the following polymers does not involve cross-linkages?
- Vulcanised rubber
- Bakelite
- Melamine
- Teflon
Answer: D (Teflon)
Question 18: Heating rubber with sulphur is known as
- Galvanisation
- Bessemerisation
- Vulcanisation
- Sulphonation
Answer: C (Vulcanisation)
Question 19: Which of the following polymers does not have vinylic monomeric units?
- Acrilan
- Nylon
- Polystyrene
- Neoprene
Answer: B (Nylon)
Question 20: Low density polythene is used in the insulation of electricity carrying wires and manufacture of flexible pipes and squeeze bottles because
- It is tough, hard and rigid
- It is chemically inert, tough, , flexible and poor conductor of electricity
- It is very tough, good conductor of electricity and flexible
- It is chemically inert, very soft, water absorbent and poor conductor of heat
Answer: B ( It is chemically inert, tough, , flexible and poor conductor of electricity)
MCQ of Chemistry in Everyday Life
Question 1: The chemical substance used to bring down body temperature in high fever are known as
- Analgesics
- Antipyretics
- Antihistamines
- Tranquilizers
Answer: B (Antipyretics)
Question 2: A drug which acts as antipyretic as well as analgesic is
- Chloroquine
- Penicillin
- Chlorodiazepoxide
- 4-acetamidophenol
Answer: D (4-acetamidophenol)
Question 3: The term broad spectrum antiboitics means
- Bactericidal antibiotics
- Bacteriostatic antibiotics
- Which kill or inhibit a wide range of gram -ve and gram +ve bacteria
- Which kill or inhibit all types of gram +ve bacteria
Answer: C ( Which kill or inhibit a wide range of gram -ve and gram +ve bacteria )
Question 4: An artificial sweetner which is derivative of sucrose is
- Saccharine
- Sucralose
- Sucrobenzamide
- Aspartame
Answer: B (Sucralose)
Question 5: The main constituents of dettol are
- Chloramphenicol + glycerol
- 2-3% solution of iodine in alcohol
- 0.2% solution of phenol
- Chloroxylenol and terpineol
Answer: D ( Chloroxylenol and terpineol )
Question 6: What is the problem faced while using alitame as artificial sweetner?
- It decomposes when added to the food item
- It provides a large number of calories to the food.
- It is difficult to control the sweetness of food while using in it.
- It increases the volume of the contents to a large extent.
Answer: C ( It is difficult to control the sweetness of food while using in it )
Question 7: The antibiotic which is effective against certain strains of cancer cells is
- Dysidazirine
- Sulphanilamide
- Vancomycin
- Ofloxacin
Answer: A (Dysidazirine)
Question 8: An antioxidant which is added to butter to increase its shelf life from months to years is
- Sodium benzoate
- Butylated hydroxy anisole
- Sulphur dioxide
- All of these
Answer: B (Butylated hydroxy anisole)
Question 9: Which is not true for a detergent molecule?
- It has non polar organic part and a polar group.
- It is not easily biodegraded.
- It is sodium salt of fatty acid.
- It is a surface active reagent.
Answer: C (It is sodium salt of fatty acid)
Question 10: The use of aspartame is limited to cold foods and drinks because
- It is unstable to heat and decomposes at cooking temperature.
- It is 500 times sweetner than cane sugar
- It becomes bitter at cooking temperature.
- It reacts with the food at cooking temperature
Answer: A ( It is unstable to heat and decomposes at cooking temperature )
Question 11: The most useful classification of drugs for medicinal chemists is
- On the basis of chemical structure
- On the basis of drug action
- On the basis of molecular targets
- On the basis of pharmacological effect
Answer: C (On basis of molecular targets)
Question 12: Glycerol is added to soap. It functions
- As a filter
- To increase lathering
- To prevent rapid drying
- To make soap granules
Answer: C (To prevent rapid drying)
Question 13: The compound that causes general antidepressant action on the central nervous system belongs to the class of
- Analgesics
- Tranquilizers
- Narcotic analgesics
- Antihistamines
Answer: B (Tranquilizers)
Question 14: Which of the following statement is not true about enzyme inhibitors?
- Inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme
- Prevent the binding of substrate
- Generally a strong covalent bond is formed between an inhibitor and an enzyme
- Inhibitors can be competitive or non competitive.
Answer: C ( Generally a strong covalent bond is formed between an inhibitor and an enzyme )
Question 15: Which of the following is a narcotic analgesic?
- Ibuprofen
- Aspirin
- Paracetamol
- Morphine
Answer: D (Morphine)
Question 16: Salol is an
- Antipyretic
- Analgesics
- Antiseptic
- Antibiotic
Answer: C (Antiseptic)
Question 17: The reaction of fat and sodium hydroxide is known as
- Dehydration
- Hydrogenation
- Saponification
- Esterification
Answer: C (Saponification)
Question 18: An ester which is used as medicine
- Ethyl acetate
- Methyl acetate
- Methyl salicylate
- Ethyl benzoate
Answer: C (Methyl salicylate)
Question 19: Which of the following destroys antigens?
- Insulin
- Antibodies
- Chromoprotein
- Phosphoprotein
Answer: B (Antibodies)
Question 20: Which one is broad spectrum antibiotic?
- Chloramphenicol
- Plasmoquin
- Xylocaine
- Antiseptic
Answer: A (Chloramphenicol)
We would love your reading of MCQs for CUET 2022 of other subjects which are as follow.
- Physical Education
- Hindustani Music Vocal
- Political Science
- Geography
- Accountancy
- Biology
- Business Studies
- Economics
- Physics
Do share this post if you liked the MCQ of Chemistry CUET. For more updates, keep logging on BrainyLads



