MCQ of Biology CUET Class 12 | Common University Entrance Test |
Table of Contents
MCQ of Biology CUET Class 12 | Common University Entrance Test
MCQ of Reproduction in Organisms
Question 1: The period from birth to the natural death of an organism signifies
- Reproductive phase
- Life cycle
- Life span
- Life style
Answer : C (Life span)
Question 2: No individual is immortal exclude
- Single celled organisms
- Green plant
- Sponges
- Drones
Answer : A (Single celled organisms)
Question 3: Clone is the product of
- Sexual reproduction
- Sexual or asexual reproduction
- Amphimixis
- Asexual reproduction
Answer : D (Asexual Reproduction)
Question 4. In monerans and protists , sexual reproduction takes place by
- Budding
- Multiple fission
- Binary fission
- Amphimixis
Answer : C (Binary fission)
Question 5. In animal and other simple organism uniparental reproduction is called_______ reproduction in plant called________ reproduction
- Vegetative , asexual
- Asexual , vegetative
- Parthenogenetic , amphimictic
- Amphimictic , apomictic
Answer : B (Asexual , vegetative)
Question 6: Which one of the following is not vegetative propagule?
- Rhizome and sucker
- Tuber and offset
- Bulbil , leaf buds , bulb
- Antherozoid
Answer : D (Antherozoid)
Question 7: Which of the following regulate the reproductive processes and the associated behavioural expression of the organisms?
- Hormones
- Environmental factors
- Abiotic components
- Interaction between hormones and the environmental factors
Answer : D (Interaction between hormones and the environmental factors)
Question 8: Oestrus cycle is seen in
- Crows and sheep
- Rats and deers
- Dogs and tiger
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 9: Birds in captivity can be made to lay eggs throughout the year in this case laying eggs is
- Related to reproduction and commercial exploitation for human welfare
- Neither related to reproduction nor a commercial exploitation for human welfare
- Not related to reproduction but a commercial exploitation for human welfare
- Related to reproduction but not a commercial exploitation for human welfare
Answer : C (Not related to reproduction but a commercial exploitation for human welfare)
Question 10: Which of the following plant exhibit unusual flowering phenomena?
- Mango and litchi
- Mango and maize
- Litchi and pea
- Bamboo species and strobilanthus species
Answer : D (Bamboo species and strobilanthus species)
Question 11. Which of the following plant do not show clear vegetative , reproductive and senescent phase ?
- Perennial plant
- Annual plant
- Biennial plant
- Either B or C
Answer : A (Perennial plant)
Question 12: Some organisms are capable of sexual and asexual reproduction under favourable condition reproduction proceeds sexually when condition become more stressful reproduction switches to sexual mode why
- Sexual mode is simple and more rapid line large number of fostering to be produced
- Sexual reproduction requires two separate individuals who can mutually provide nutrient support during stress
- Sexual reproduction produce individuals with new combination of recombined chromosome increase diversity
- Asexual reproduction requires more energy
Answer : C (Sexual reproduction produce individuals with new combination of recombined chromosome increase diversity)
Question 13: The fastest method to obtain clones is through
- Induced mutation
- Para sexual hybridization
- Parthenogenesis
- Vegetative reproduction
Answer : D (Vegetative reproduction)
Question 14: Internal fertilization occurs in
- Many fungi
- Reptiles and mammals
- Bryophytes, pteridophytes gymnosperms and angiosperms
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 15: In Heterogamous organism the male gamates and female gametes are called respectively
- Spermatogonia , oogonia
- Spermatid , ootid
- Sperm , ovum
- Sperm and oospore
Answer : C (Sperm , ovum )
Question 16: In which of the following water is essential for fertilization
- Algae
- Bryophytes
- Pteridophytes
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 17: In majority of organisms male gamete is _____ and female gamete is______
- Motile , motile
- Non – motile , non – motile
- Non – motile , motile
- Motile , non motile
Answer : D (Motile , non – motile)
Question 18: Offspring of oviparous animals are at a greater risk as compared to offspring of various animals because
- Proper embryonic care and protection is lesser
- Embryo is not developed
- Progenies are with more variation
- Progenies are larger
Answer : A (Proper embryonic care and protection is lesser)
Question 19: Which of the following statement is true about water hyacinth?
- It gives product to be used in medicine
- It is a marine plant
- It take oxygen from water which causes death of fishes
- It is being cultivated in seawater for biogas
Answer : C (It take oxygen from water which causes death of fishes)
Question 20: Monoecious plant of chara shows occurrence of
- Stamen and carpel on the same plant
- Upper antheridium and lower oogonium on the same plants
- Upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant
- Antheridiophore and Archegoniophore on same plant
Answer : C (Upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant)
Question 21: Zoospores are
- Motile gametes of chlamydomonas
- Non motile gametes of sponges
- Motile gametes of hydra
- Non motile gametes of penicillium
Answer : A (Motile gamates of Chlamydomonas)
Question 22: Asexual reproductive structures found in Penicillium are
- Conidia
- Buds
- Gemmules
- Zoospore
Answer : A (Conidia)
Question 23: Which of the following pairs is not correctly match?
Mode of reproduction Example
- Offset Water Hyacinth
- Rhizome Banana
- Binary fission Sargassum
- Conidia Penicillium
Answer : C (Binary fission Sargassum)
Question 24: Gemmule formation is a common mode of reproduction in
- Hydra
- Sponge
- Penicillium
- Amoeba
Answer : B (Sponge)
Question 25: Strobilanthus kunthiana is also called
- Neela kuranji
- Peela kuranji
- Hara kuranji
- Kala kuranji
Answer : A (Neela kuranji)
Question 26: Oestrus cycle is cyclic change in the activities of ovaries and accessory duct in non primates during
- Reproductive period
- Maturation period
- Ageing period
- Juvenile period
Answer : A (Reproductive period)
Question 27: Those organisms which reproduce throughout the year are commonly known as ____ breeders; eg.____ which those which displays reoccurring sexual activity are called_____ breeders; eg._____
- Continuous , sparrow , seasonal , hen
- Seasonal , lizard , continuous , hen
- Continuous , lizard , seasonal , tiger
- Seasonal , lizard , continuous , tiger
Answer : A (Continuous , sparrow , seasonal , hen)
Question 28: Name the type of gametes found in algae
- Homogamates
- Heterogamates
- Anisogametes
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 29: Under a heterogametic condition male gamete is commonly known as
- Antherozoid
- Sperm
- Egg
- Both A and B
Answer : D (Both A and B)
Question 30: The condition wherein male and female parts are present on variable plants is called
- Heterothallic
- Dioecious
- Unisexual
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 31: The condition wherein both male and female reproductive organs are found on the identical plant is called
- Unisexual
- Bisexual
- Monoecious
- Both B and C
Answer : D (Both B and C)
Question 32: Which one of the succeeding is hermaphrodite?
- Ant
- Aphids
- Earthworm
- Cockroach
Answer : C (Earthworm)
Question 33: Which of the following statement regarding pollination is accurate ?
- Mostly occur in dioecious plants
- Facilitates Pollen transfer to stigma
- Both A and B
- None of the above
Answer : C ( Both A and B)
Question 34: Parthenogenesis is the process wherein new organism is formed
- With fertilization
- Without fertilization
- Through mitosis
- Through meiosis
Answer : B (Without fertilisation)
Question 35: Why does organisms demonstrating external fertilization liberates a high number of gametes ?
- This is because greater synchrony is shown by these organisms among the sexes
- In order to enhance the chances of syngamy
- To produce large number of Off springs as they are vulnerable to predators.
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 36: Choose the incorrect pair
- Cell division in embryo – increase the number of cells
- Cell differentiation – form specialised tissues and organs
- Eggs covered by hard calcareous shell – oviparous animals
- Zygote develops outside the body – viviparous animals
Answer : D (Zygote develops outside the body – viviparous animals)
Question 37: Probability of survival of young ones are greater in the case of ______ individuals.
- Oviparous
- Viviparous
- Ovoviviparous
- None of these
Answer : B (Viviparous)
MCQ of Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
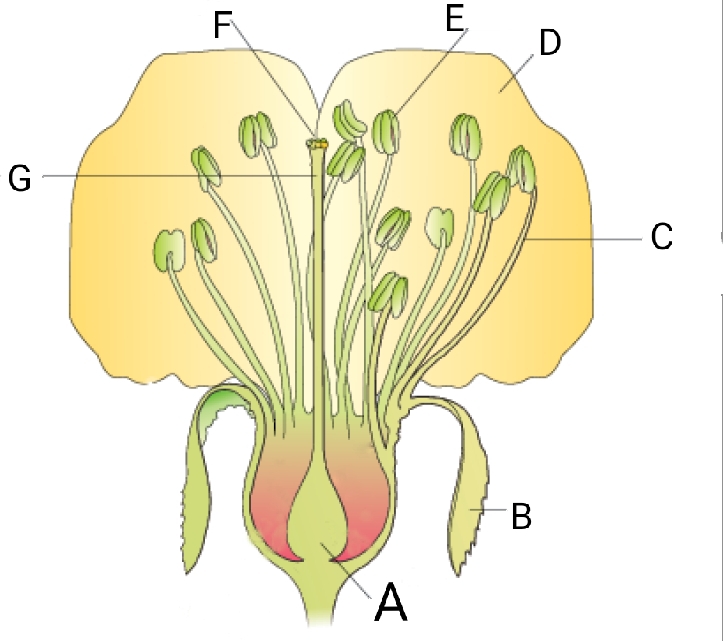
Question 1: Identify A to G in following figure and answer accordingly.
- A – Ovary , B – Filament , C – sepal , D – Petal , E – Style , F – Stigma , G – Anther
- A – Sepal , B – Ovary , C – Petal , D – Filament , E – Anther , F – Stigma , G – Style
- A – Ovary , B – Sepal , C – Filament , D – Petal , E – Anther , F – Stigma , G – Style
- A – Petal , B – Anther , C – Stigma , D – Style , E – Filament , F – Sepal , G – Ovary
Answer : C (A – Ovary , B – Sepal , C – Filament , D – Petal , E – Anther , F – Stigma , G – Style)
Question 2: The Terminal structure of stamen is called
- Pollen
- Filament
- Anther
- All of these
Answer : C (Anther)
Question 3: Male gametophyte in angiosperms produces
- Two sperms and a vegetative cell
- Single sperm and a vegetative cell
- Single sperm and two vegetative cell
- Three sperms
Answer : A (Two sperms and a vegetative cell)
Question 4: The lengthwise running groove on and anther which separate theca is called
- Rupture line
- Line of dehiscence
- Suture of Anther
- None of these
Answer : B (Line of dehiscence)
Question 5: Number of microsporangia in angiosperm anther is
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer : D (4)
Question 6: Microsporangium develops into
- Pollens
- Microgamates
- Megagamates
- Pollen sac
Answer : D (Pollen sac)
Question 7: The innermost layer of microsporangium is
- Tapetum
- Endothecium
- Middle layer
- Epidermis
Answer : A (Tapetum)
Question 8: Centre of each microsporangium is occupied by
- Sporogenous tissue
- Tapetum
- Central tissue
- Microspore mother cell
Answer : A (Sporogenous tissue)
Question 9: Which of the following perform microsporogenesis?
- Microspore mother cell
- Pollen mother cell
- Both A and B
- None of the above
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 10: Microspore tetrad (pollen grains)is a result of
- Mitotic cell division
- Meiotic cell division
- Both A and B
- None of these
Answer : B (Meiotic cell division)
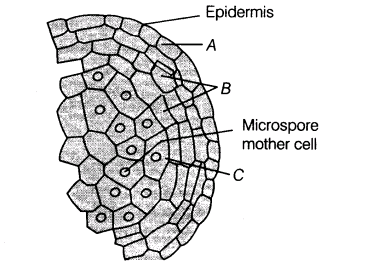
Question 11: The above diagram is enlarged view of one microsporangium of a mature anther identify A , B , C –
- A – Middle layer , B – Endothecium , C – Tapetum
- A – Endothecium , B – Tapetum , C – Middle layer
- A – Endothecium , B – Middle layer , C – Tapetum
- A – Tapetum , B – Middle layer , C – Endothecium
Answer : C (A – Endothecium , B – Middle layer , C – Tapetum)
Question 12: The proximal part of filaments of stamen is attached to
- Thalamus or the petal
- Sepals or thalamus
- Pedicle aur petiole
- Ovary or Ovule
Answer : A (Thalamus or the petal)
Question 13: Pollens have two prominant walls which are A and B here A and B refers to
- A – Intine B – Protein coat
- A – Exine B – Intine
- A – Sporopollenin B – Intine
- A – Sporopollenin B – Exine
Answer : B (A – Exine B – Intine)
Question 14: The sporopollenin is known degradable because
- It can withstand strong acids
- It is resistant at very high temperature
- No enzyme degrade it
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 15: Intine is made up of
- Cellulose
- Pectin
- Both A and B
- Protein
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 16: Which cell is bigger and have abundant food reserve material during microsporogenesis?
- Generative cell
- Vegetative cell
- Vacuole
- Spore mother cell
Answer: B (Vegetative cell)
Question 17: 60% of the angiosperms shed their pollens at the
- 2 – celled stage
- 3 – celled stage
- 4 – celled stage
- 1- celled stage
Answer: A (2 – celled stage)
Question 18: Function of filiform apparatus is to
- Recognise the suitable Pollen at stigma
- Stimulate division of generative cell
- Produce nectar
- Guide the entry of pollen tube
Answer : D (Guide the entry of pollen tube)
Question 19: Pollens are stored at which temperature
- -196°C
- 196°C
- 10°C
- 0°C
Question 20: The stalk which joins ovule and placenta is called
- Funicle
- Helium
- Chalaza
- Micropyle
Answer : A (Funicle)
Question 21: Embryo sac is also called
- Female gamete
- Synergids
- Female gametophyte
- Egg of angiosperm
Answer : C (Female gametophyte)
Question 22: Megasporogenesis is
- Formation of root
- Formation of seeds
- Formation of megaspore
- Both B and C
Answer : C (Formation of megaspore)
Question 23: Each cell of sporogenous tissue in anther is
- Microspore
- Pollen
- Potential Pollen or microspore mother cell
- Megaspore mother cell
Answer : C (Potential pollen or microspore mother cell)
Question 24: As the anther mature and dehydrate the ____ separate dissociate from each other and develop into ______
- Megaspore , embryo sac
- Microspore , pollen grains
- Pollen grain , megaspore
- Megaspore , microspore
Answer : B (Microspore , pollen grains)
Question 25: Identify A to F in the diagram.
- A – Egg , B – Filiform apparatus , C – Synergid , D – Antipodal cell , E – Polar nuclei , F – Central cell
- A – Egg , B – Synergid , C – Filiform apparatus , D – Antipodal cell , E – Central cell , F – Polar nuclei
- A – Central cell , B – Synergid , C – Synergid , D – Antipodal cell , E – Filiform apparatus , F – Polar nuclei
- A – Filiform apparatus , B – Synergid , C – Egg , D – Central cell , E – Polar nuclei , F – Antipodal cell
Answer : D (A – Filiform apparatus , B – Synergid , C – Egg , D – Central cell , E – Polar nuclei , F – Antipodal cell)
Question 26: Two nuclei with one cell are found in
- Antipodal cell
- Chalazal cell
- Central cell
- Synergid cell
Answer : C (Central cell)
Question 27: Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to stigma of another flower of different plant is called
- Geitonogamy
- Xenogamy
- Chasmogamy
- Cleistogamy
Answer : B (Xenogamy)
Question 28: In Chasmogamy , pollination takes place in
- Open flower
- Close flower
- Large flower
- Geitonogamy flower
Answer : A (Open flower)
Question 29: The most common abiotic pollinating agency in flowering plant is
- Water
- Wind
- Both A and B
- None of these
Answer : B (Wind)
Question 30: Advantage of cleistogamy is
- Higher genetic variability
- More vigorous of offspring
- No dependence on pollinators
- Vivipary
Answer : C (No dependence on pollinators)
Question 31: Characteristics of wind pollinated pollens is , they are
- Non – sticky
- Light
- Large number in production
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 32: Continued self pollination results in
- Inbreeding depression
- Outbreeding depression
- Hybrid vigour
- Better result in offsprings
Answer : A (Inbreeding depression)
Question 33: Unisexual or dioecious condition prevents
- Autogamy
- Geitonogamy
- Self fertilization
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 34: Fertilization involving carrying of male gamate by pollen tube is
- Porogamy
- Siphonogamy
- Chalazagamy
- Synganogamy
Answer : B (Siphonogamy)
Question 35: Geitonogamy involves
- Fertilization of a flower by the Pollen from another flower of the same plant
- Fertilization of a flower by the Pollen from the same flower
- Fertilization of a flower by the Pollen from a flower of another plant in the same population
- Fertilization of a flower by the Pollen from a flower of another plant belonging to a distant population
Answer : A (Fertilization of a flower by the pollen from another flower of the same plant)
Question 36: Polar nuclei are located in
- Pollen tube
- Embryo sac
- Ovule
- Thalamus
Answer : B (Embryo sac)
Question 37: Generally Pollen tube enters through
- Micropylar region
- Antipodal region
- Chalazal end
- Nuclear region
Answer : A (Micropylar region)
Question 38: Number of chromosomes in gamate mother cell is 24, then find out the chromosome number of male and female gamete.
- 18 , 18
- 17 , 18
- 20 , 20
- 12 , 12
Answer : D (12 , 12)
Question 39: PEC (primary endosperm cell) is formed
- After triple fusion
- Before triple fusion
- At the time of syngamy
- Always persisted
Answer : A (After triple fusion)
Question 40: Gametogenesis in haploid plant involves
- Binary fission
- Meiosis
- Mitosis
- Amitosis
Answer : C (Mitosis)
Question 41: In angiosperm , Pollen tube liberate their male gamates into the
- Central cell
- Antipodal cell
- Egg cell
- Synergids
Answer : D (Synergids)
Question 42: Out of the following choose the post fertilization event.
- Endospermogenesis
- Embryogenesis
- Both A and B
- Organogenesis
Answer : C (Both A and B )
Question 43: Which of the following sequence of development of embryo sac is correct?
- Nucellus → megaspore→ embryo sac
- Nucellus → megagametophyte → megaspore → embryo sac
- Nucellus → megasporangium → megaspore → embryo sac
- Nucellus → megaspore mother cell → megaspore → embryo sac
Answer : D (Nucellus→ megaspore mother cell → megaspore → embryo sac)
Question 44: Perisperm is
- Outer part of embryo sac
- Degenerate synergid
- Degenerate secondary nucleus
- Remains of nucellus
Answer : D (Remains of nucellus)
Question 45: Function of suspensor in embryo is
- Absorption of nourishment
- Push the embryo into nuritive endosperm region
- Formation of secondary embryo
- All of the above
Answer : B (Push the embryo into nutritive endosperm region)
Question 46: An ovule has generally how many embryo sac ?
- 1
- 3
- 4
- 8
Answer : A (1)
Question 47: The female gametophyte of dicot or monosporic embryo sac is –
- 7 celled 7 nucleated
- 8 celled 7 nucleus
- 7 celled 8 nucleate
- 8 celled and 7 nucleate
Answer : C (7 – celled and 8 – nucleate)
Question 48: Autogamy is
- Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of the same flower
- Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of the another flower
- Pollination between two flower
- Maturation of anther and stigma at different times
Answer : A (Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of the same flower)
Question 49: Cleistogamous flower produces assured seed set even in the absence of pollinator. why?
- Because they have fragnance
- Because they remain open
- Because they are autogamous
- Because they are colourful
Answer : C (Because they are autogamous)
Question 50: This of the following devices is not used by plants to prevent autogamy –
- Self incompatibility
- Production of unisexual flower
- Heterostyly
- Production of cleistogamous flowers
Answer : D (Production of cleistogamous flowers)
Question 51: Which is not diploid?
- Nucellus
- Integuments
- Endosperm
- Embryo
Answer : C (Endosperm)
Question 52: In dicot embryo the radical is formed by
- Epibasal tier of embryo
- Hypobasal tier of embryo
- Hypophysis of suspensor
- Terminal cell of suspensor
Answer : C (Hypophysis of suspensor)
Question 53: Identify the A to E in following diagram of typical dicot embryo.
- A – Cotyledons , B – Hypocotyle , C – Plumule , D – Root , E – Radicle
- A – Radicle , B – Root cap , C – Plumule , D – Hypocotyle , E – Cotyledons
- A – Hypocotyle , B – Cotyledons , C – Plumule , D – Radicle , E – Root cap
- A – Plumule , B – Cotyledons , C – Hypocotyle , D – Radicle , E – Root cap
Answer : D (A – Plumule , B – Cotyledons , C – Hypocotyle , D – Radicle , E – Root cap)
Question 54: Development of embryo from a cell of embryo sac other than egg is an example of
- Apospory
- Apogamy
- Adventitive embryogeny
- Parthenogenesis
Answer : C ( Adventitive embryogeny)
Question 55: Maturation of stigma and another at different time in the same flower is
- Heterostyle
- Dichogamy
- Dicliny
- Herkogamy
Answer : B (Dichogamy)
Question 56: Movement of pollen tube towards embryo sac is
- Thermotactic
- Phototactic
- Chemotactic
- Thigmotatic
Answer : C (Chemotactic)
Question 57: False fruit is a fruit in which
- Only ovary take part in fruit development
- Only embryo take part in fruit development
- Only chalazal cells take part in fruit development
- Ovary and other floral part included in fruit
Answer : D (Ovary and other floral part included in fruit)
Question 58: Type of cell division takes place in apomixis is
- Reductional
- Meiosis
- Both A and B
- Mitosis
Answer : D (Mitosis)
Question 59: Occurrence of more than one embryo is called
- Polyembryony
- Embryony
- Parthenogenesis
- Fertilization
Answer : A (Polyembryony)
Question 60: Milky water of green coconut is
- Liquid chalaza
- Liquid Nucleus
- Liquid female gametophores
- Liquid endosperm
Answer : D (Liquid endosperm)
Question 61: Germ pore is the area where exine is
- Thick
- Thick and uniform
- Uniform
- Absent
Answer : D (Absent)
Question 62: Pollen kit is formed from
- Endothecium
- Middle layer
- Microspore mother cell
- Tapetum
Answer : D (Tapetum)
Question 63: Remnants of nucellus present in seed are called
- Pericarp
- Periderm
- Endosperm
- Perisperm
Answer : D (Perisperm)
Question 64: A seed is formed from
- Ovule
- Embryo
- Embryo sac
- Ovary
Answer : A (Ovule)
Question 65: Perisperm differ from endosperm in
- Having no reserve food
- Being a diploid tissue
- Its formation by fusion of secondary nucleus with several sperms
- Being a haploid tissue
Answer : B (Being a diploid tissue)
MCQ Of Human Reproduction
Question 1: Which of the following is a secondary sex organ ?
- Beard
- Uterus
- Ovary
- Broad hips
Answer : B (Uterus)
Question 2: Secondary sexual characters in females are due to :
- Estrogens
- Androgens
- Progesterone
- Cholecystokinin
Answer : A (Estrogens)
Question 3: Scrotal sacs are connected with abdominal cavity by
- Vaginal cavity
- Inguinal canal
- Spermatic canal
- Haversian canal
Answer : B (Inguinal canal)
Question 4: The testis in humans are situated outside the abdominal cavity inside a pouch called scrotum the purpose served is for
- Acceleration of maturation of sperms
- Providing more space for the growth of epididymis
- Escaping any possible compression by the visceral organs
- Maintaining the scrotal temperature lower than the internal body temperature
Answer : D (Maintaining the scrotal temperature lower than the internal body temperature)
Question 5: In most mammals, the testes are located in scrotal sac for
- Spermatogenesis
- Sex differentiation
- More space to visceral organs
- Independent functioning of kidney
Answer : A (Spermatogenesis)
Question 6: In mammals failure of testes to descend into the scrotum is known as
- Castration
- Impotency
- Paedogenesis
- Cryptorchidism
Answer : D (Cryptorchidism)
Question 7: The tunica albuginea is a covering around the
- Testis
- Ovaries
- Scrotal sacs
- Epididymis
Answer : A (Testis)
Question 8: Sperms are produced in
- Vas deferens
- Prostate gland
- Interstitial cells
- Seminiferous tubules
Answer : D (Seminiferous tubules)
Question 9: Which of the following is found in the interstitial connective tissue of testis ?
- Sertoli cells
- Sustencular cells
- Leydig cells
- Chromaffin cells
Answer : C (Leydig cells)
Question 10: Location of leydig cells and their secretions are
- Ovary–Estrogen
- Liver–Cholestrol
- Testis–Testosterone
- Pancreas–Glucagon
Answer : C (Testis–Testosterone)
Question 11: In the vertebrate testis, for Nourishment during spermiogenesis the spermatids get attached to
- Sertoli cells
- Spermatocytes
- Interstitial cells
- Sperm – mother cells
Answer : A (Sertoli cells)
Question 12: Sertoli cells are found in testis, these cells are
- Nurse cells
- Reproductive cells
- Receptor cells
- None of these
Answer : A (Nurse cells)
Question 13: Which of the following controls the function of sertoli cells?
- FSH
- ACTH
- Estrogen
- Testosterone
Answer : A (FSH)
Question 14: Rete testis opens to
- Urethra
- Vasa efferentia
- Bidder’s canal
- Cauda epididymis
Answer : B (Vasa efferentia)
Question 15: If the vas differentia of a man are surgically cut or blocked:
- Semen will be without sperms
- Spermatogenesis will not take place
- Testosterone will disappear from blood
- Sperms in the semen become non motile
Answer : A (Semen will be without sperms)
Question 16: Which gland in mammal makes alkaline secretion for lubrication ?
- Testis
- Pineal body
- Prostate gland
- Cowper’s gland
Answer: D (Cowper’s gland)
Question 17: Seminal fluid contains the secretions of
- Follicles, uterus and prostate gland
- Prostate cowper’s and bartholin’s gland
- Seminal vesicle, uterus and prostate gland
- Seminal vesicle, prostate and Cowper’s gland
Answer : D (Seminal vesicle, prostate and Cowper’s gland)
Question 18: Seminal fluid has a pH of about
- 6.0
- 7.4
- 8.5
- 9.0
Answer : B (7.4)
Question 19: Which one is unpaired gland in male reproductive system ?
- Seminal vesicle
- Cowper’s gland
- Prostate gland
- Lacrimal gland
Answer : C (Prostate gland)
Question 20: Which of the following sugars in semen is a source of energy for the spermatozoa ?
- Sucrose
- Fructose
- Glucose
- Galactose
Answer : B (Fructose)
Question 21: At what speed human sperm moves in the female genital tract ?
- 3 mm/min
- 10 mm/min
- 15 mm/min
- 20 mm/min
Answer : A (3 mm/min)
Question 22: The blood vessels and nerves enter the ovary through
- Hilum
- Zona pellucida
- Antrum
- Graafian follicle
Answer : A (Hilum)
Question 23: Match the following :
A Inguinal canal 1 Network of seminiferous tubules
B Rete testis 2 Secondary sexual character
C Leydig cells 3 For descending of testis
D Prepuce 4 Dorsal bundles of muscles
E Corpora cavernosa 5 Terminal skin of penis
- A = 1, B = 2, C = 3, D = 5, E = 4
- A = 3, B = 1, C = 4, D = 2, E = 5
- A = 2, B = 4, C = 3, D = 5, E = 1
- A = 3, B = 1, C = 2, D = 5, E = 4
Answer : D (A = 3, B = 1, C = 2, D = 5, E = 4)
Question 24: Graafian follicle possess :
- Theca externa
- Granulosa
- Theca interna
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 25: The growth and maturation of Graafian follicle is controlled by
- FSH-LH
- GH-ADH
- FSH-LTH
- LH-ACTH
Answer : A (FSH-LH)
Question 26: The release of mature ovum from Graafian follicle is known as
- Oogenesis
- Oviparity
- Ovulation
- Oviposition
Answer : C (Ovulation)
Question 27: Which is the correct sequence of layers in the mammalian egg from outside to inside ?
- Zona pellucida, Corona radiata, plasma membrane
- Corona radiata, zona pellucida, plasma membrane
- Plasma membrane, zona pellucida, Corona radiata
- None of the above
Answer : B (Corona radiata, zona pellucida, plasma membrane)
Question 28: When is progesterone secreted ?
- After ovulation
- After parturition
- Before ovulation
- At the time of parturition
Answer : A (After ovulation)
Question 29: An important function of progesterone is
1 Prepare uterus for pregnancy
2 Implantation of embryo
3 Maintenance of pregnancy
4 Stimulate ADH
Answer codes
- 1 and 2 are correct
- 2 and 4 are correct
- 1 and 3 are correct
- 1,2 and 3 are correct
Answer : D (1,2 and 3 are correct)
Question 30: Labia majora of a female mammal is homologous to
- Scrotal sac
- Epididymis
- Prostate gland
- Seminal vesicle
Answer : A (scrotal sac)
Question 31: If a germ cell in a female gonads and germ cell in the male gonad begin undergoing meiosis simultaneously what will be the ratio of ova and sperms produced?
- 1: 1
- 1 : 2
- 1 : 4
- 2 : 1
Answer : C ( 1 : 4 )
Question 32: Correct sequence of cell stages in spermatogenesis is:
- Spermatocytes, spermatids, spermatogonia, spermatozoa
- Spermatogonia, spermatocytes, spermatids, spermatozoa
- Spermatocytes, spermatogonia, spermatids, spermatozoa
- Spermatogonia, spermatids, spermatocytes, spermatozoa
Answer : B (spermatogonia , spermatocytes , spermatids , spermatozoa)
Question 33: Number of spermatozoa produced by a single primary spermatocyte during spermatogenesis is
- One
- Two
- Four
- Eight
Answer : C (Four)
Question 34: Conversion of spermatid to spermatozoa is called
- Cytokinesis
- Vitellogenesis
- Spermiogenesis
- Spermatogenesis
Answer : C (Spermiogenesis)
Question 35: The head of sperm consists of
- Nucleus
- Acrosome
- Mitochondria
- Acrosome and nucleus
Answer : D (Acrosome and nucleus)
Question 36: The acrosome plays important role in
- Penetration of ovum by sperm
- Providing energy to sperm
- Motility of sperm
- None of the above
Answer : A (Penetration of ovum by sperm)
Question 37: The lytic enzyme released by sperm is
- Ligase
- Acrosome
- Androgamone
- Hyaluronidase
Answer : D (Hyaluronidase)
Question 38: Middle piece of mammalian sperm contains
- Centrioles only
- Mitochondria only
- Nucleus and mitochondria
- Centrioles and mitochondria
Answer : D (Centrioles and mitochondria)
Question 39: A cross section at the midpoint of the middle piece of a human sperm will show
- Centriole and mitochondria
- 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules only
- Mitochondria and 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules
- Centriole , mitochondria and 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules
Answer : C (Mitochondria and 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules)
Question 40: Oogenesis comprises
- Maturation phase
- Growth phase
- Multiplication phase
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 41: During oogenesis each diploid cell produces
- Four functional cells
- Four non functional polar bodies
- One functional egg and three polar bodies
- Two functional eggs and two polar bodies
Answer : C (One functional egg and three polar bodies)
Question 42 : First polar body is formed at which stage of oogenesis
- First meiosis
- Second mitosis
- First mitosis
- Differentiation
Answer : A (First meiosis)
Question 43: In which phase of cell division is oocyte arrested
- Interphase
- Prophase I
- Anaphase II
- Both Prophase I and II
Answer : B (Prophase I)
Question 44: During oogenesis in mammals , the second miotic division occurs
- Before ovulation
- After fertilization
- In the formation of the primary oocyte
- In the formation of the secondary oocyte
Answer : B (After fertilization)
Question 45: Which one of the following is haploid?
- Oogonia
- Primary oocyte
- Secondary oocyte
- Primary spermatocyte
Answer : C (Secondary oocyte)
Question 46: In the human female , menstruation can be deferred by the administration of
- LH only
- FSH only
- Combination of FSH and LH
- Combination of estrogen and progesterone
Answer : D (Combination of estrogen and progesterone)
Question 47: Which of the following hormones is active during proliferative phase of menstrual cycle ?
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
- Testosterone
- All of these
Answer : A (Estrogen)
Question 48: The phase of menstrual cycle in humans that lasts for 7 to 8 days is
- Luteal phase
- Mensuration
- Follicular phase
- Ovulatory phase
Answer : C (Follicular phase)
Question 49: Ovulation in females is under the control of
- LTH
- ADH and LH
- FSH and LH
- LTH and TSH
Answer : C (FSH and LH)
Question 50: Shortest phase in the menstruation cycle of women is:
- Menses
- Luteal phase
- Follicular phase
- Ovulatory phase
Answer : D ( Ovulatory phase)
Question 51: Which hormone level reaches peak during luteal phase of menstrual cycle ?
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
- Luteinizing hormone
- Follicle stimulating hormone
Answer : B ( Progesterone)
Question 52: Uterine endometrium , uterine glands and connective tissue are broken during menstrual phase. This is due to
- Lack of Estrogen
- Lack of progesterone
- Oversecretion of FSH
- Over production of progesterone
Answer : B (Lack of progesterone)
Question 53: in the absence of pregnancy , Corpus luteum
- Degenerates after sometime
- Is maintained by progesterone
- Becomes active , secrets FSH and LH
- Produces a lot of oxytocin and relaxin
Answer : A (Degenerates after some time)
Question 54: Which of the following events is correctly matched with the time period in a normal menstrual cycle ?
- Release of egg – 5th day
- Endometrium regenerates – 5 – 10 days
- Rise in progesterone level – 1 – 15 days
- Endometrium secrets nutrients for implantation – 11 – 18 days
Answer : B (Endometrium regenerates – 5 – 10 days)
Question 55: Cessation of menstrual cycle is termed as
- Menarche
- Menopause
- Impotency
- None of these
Answer : B (Menopause)
Question 56: Maturation of sperm before penetration of ovum is called
- Ovulation
- Spermatid
- Capacitation
- None of these
Answer : C (Capacitation)
Question 57: Fertilization of sperm and ovum takes place in
- Ampulla of oviduct
- Isthmus of oviduct
- Fimbriae of oviduct
- None of these
Answer : A (Ampulla of oviduct)
Question 58: The embryo at 16 – celled stage is known as
- Morula
- Gastrula
- Blastula
- Blastomere
Answer : A (Morula)
Question 59: Which germ layer develops first during embryonic development ?
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- Both B and C
Answer : C (Endoderm)
Question 60: A mammalian blastula is called
- Embryo
- Blastocyst
- Trophoderm
- Blastomere
Answer: B (Blastocyst)
Question 61: The attachment and development of embryo inside uterus is called
- Gestation
- Conception
- Impregnation
- Implantation
Answer : D (Implantation)
Question 62: First or free milk is called
- Rostrum
- Colostrum
- Cholesterol
- Babies milk
Answer : B (Colostrum)
Question 63: Signals from fully developed foetus and parturition ultimately lead to parturition which requires the release of
- Relaxin from placenta
- Estrogen from placenta
- Oxytocin from foetal pituitary
- Oxytocin from maternal pituitary
Answer : D (Oxytocin from maternal pituitary)
Question 64: In human cleavage divisions are
- Fast and synchronous
- Slow and synchronous
- Fast and asynchronous
- Slow and asynchronous
Answer : D (Slow and asynchronous)
Question 65: The main function of the fimbriae of the fallopian tube in females is to
- Help in development of ovary
- Help in the development of Corpus luteum
- Release to ovum from the Graafian follicle
- Help in the collection of the ovum after ovulation
Answer : D (Help in the collection of the ovum after ovulation)
Question 66: Which one of the following is initiated by secretion of trophoblast ?
- Cleavage
- Blastulation
- Gastrulation
- Implantation
Answer : D (Implantation)
MCQ Of Reproductive Health
Question 1: Reproductive health is the well – being of ?
- Physical aspects
- Emotional and behavioral aspects
- Social aspects
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 2: Amniocentesis is the detection of?
- Chromosomal pattern by taking amniotic fluid
- Chorionic fluid from developing embryo
- Chromosomal pattern after childbirth
- Chromosomal pattern before fertilization
Answer : A (Chromosomal pattern by taking amniotic fluid)
Question 3: In context of amniocentesis, which of the following statement is incorrect?
- It is used for prenatal sex determination
- It can be used for detection of Down syndrome
- It can be used for detection of cleft palate
- It is usually done when a woman in between 14 – 16 weeks pregnant
Answer : C (It can be used for detection of cleft palate)
Question 4: Identify the incorrect statement from those given below?
- RCH programmes created awareness among people about various reproduction related aspects
- Sexually transmitted diseases can be avoided by educating people with proper information about reproduction, adolescence and related changes, etc.
- Ultrasounds have been banned as it was used for foetal sex determination based on chromosomal studies
- None of the above
Answer : C (Ultrasounds have been banned as it was used for foetal sex determination based on chromosomal studies)
Question 5: Which of the following cannot be detected in a developing foetus by amniocentesis?
- Klinefelter’s syndrome
- Sex of the foetus
- Down’s syndrome
- Jaundice
Answer : D (Jaundice)
Question 6: Indicators of the improved reproductive health of the society are?
- Better detection and cure of STDs
- Improved medical facilities
- Decreased maternal and infant mortality rates
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 7: Population explosion is?
- Increased frequency of diseases in population
- Rapid increase in population number
- Rapid decrease in population number
- None of the above
Answer : B (Rapid increase in population number)
Question 8: Select the correct option which includes the steps implemented by government to control the ever increasing population?
- Increasing the price of contraceptives so they are available to all
- Advertising the benefits of small family, slogans like, “hum do hamare do’, etc
- Raising the marriageable age, females 18 years, males 21 years
- Both B and C
Answer : D (Both B and C)
Question 9: An ideal contraceptive should be?
- User friendly
- Reversible
- Both A and B
- Increase sexual drive
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 10: Natural methods of contraception are the natural ways to?
- Increase spermicidal activity
- Prevent fertilisation
- Decrease mortality
- Increase mortality
Answer : B (Prevent fertilisation)
Question 11: Days of periodic abstinence are?
- 10 – 11 days of menstrual phase
- 10 – 17 days of menstrual phase
- 17 – 20 days of menstrual phase
- 20 – 28 days of menstrual phase
Answer : B (10 – 17 days of menstrual phase)
You may also read MCQ of Reproduction in Organisms, MCQ of Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants, MCQ of Human Reproduction, MCQ Of Principles of Inheritance and Variation, MCQ of Molecular Basis of Inheritance for better understanding of the chapters.
Question 12: Periodic abstinence is avoiding sex during?
- Follicular phase
- Ovulatory phase
- Menstrual phase
- None of the above
Answer : B (Ovulatory phase)
Question 13: Coitus interruptus is the withdrawl method of natural contraception involving
- Withdrawl of penis before ejaculation
- Withdrawl of penis after ejaculation
- Sex during ovulation
- No sex during ovulation
Answer : A (Withdrawl of penis before ejaculation)
Question 14: Lactational amenorrhea is
- Absence of menses in adult age
- Absence of menses in elderly age
- Absence of menses during lactation
- No menses during pregnancy
Answer : C (Absence of menses during lactation)
Question 15: Condoms or femidoms are made up of thin rubber/latex sheath which is used to cover?
- Penis in male
- Cervix in female
- Both A and B
- None of these
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 16: Diaphragms, cervical caps and vaults are?
- Non-usable
- For female use only
- For male use only
- None of these
Answer : B (For female use only)
Question 17: Spermicidal creams are used in addition to condoms, diaphragms, cervical cap and vaults for?
- Lubrication
- Killing germs
- Increasing contraceptive effectiveness
- None of the above
Answer : C (Increasing contraceptive effectiveness)
Question 18: IUDs stands for?
- Inter Uterine Devices
- Intra Uterine Devices
- Inter Uterine Development
- Intra Uterine Development
Answer : B (Intra Uterine Devices)
Question 19: Which IUD increases the phagocytosis of the sperms within the uterus?
- Non-medicated IUD
- Copper releasing IUD
- Both A and B
- Hormone releasing IUD
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 20: Example of the non-medicated IUD is?
- Cu – T
- Cu – 7
- Multiload – 375
- Lippes loop
Answer : D (Lippes loop)
Question 21: Hormone releasing IUDs among the following are?
- Copper – T
- LNG – 20
- Saheli
- Diaphragm
Answer : B (LNG – 20)
Question 22: Copper releasing IUDs are used for suppressing the?
- Activity of ova
- Activity of the uterus
- Motility of the sperms
- Motility of ova
Answer : C (Motility of the sperms)
Question 23: Example of copper releasing IUD are?
- Cu – T
- C4 – 7
- Multiload – 375
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 24: In IUD contraception, sperm motility decreases due to?
- Cu ions
- Fe ions
- Zn ions
- Se ions
Answer : A (Cu ions)
Question 25: …A… makes the uterus unsuitable for implantation and the cervix hostile to …B… ?
- A – Hormonal releasing IUD; B – spermatogonia
- A – Hormonal releasing IUD; B – sperms
- A – Sperms, B hormonal releasing IUD
- A – Sperms, B – ova
Answer : B (A – Hormonal releasing IUD; B – sperms)
Question 26: Oral contraceptives have hormonal preparation of ?
- Progesterone
- Estrogen
- Both A and B
- None of these
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 27: Oral contraceptives inhibits …A… and implantation as well as quality of cervical …B… to prevent the entry of sperms?
- A – ovulation; B – mucus
- A – oogenesis; B – structure
- A – oogenesis; B – nucleus
- A – spermatogenesis; B – mucus
Answer : A (A – ovulation; B – mucus)
Question 28: Pills have to be taken daily for period of …A… days. Starting preferably within first five days of menstrual cycle. After a gap of …B… days, it has to be repeated in the same pattern?
- A – 27; B – 1
- A – 21; B – 7
- A – 22; B – 5
- A – 24; B – 4
Answer : B (A – 21; B – 7)
Question 29: Administration of progesterone, progesterone – estrogen combination and IUDs are effective with in?
- 72 hours
- 48 hours
- 24 hours
- 96 hours
Answer : A (72 hours)
Question 30: Injections and implants (the progesterone or progesterone – estrogen combination) are used by the females usually under the?
- Skin of the inner arm above elbow
- Vagina
- Upper skin of stomach
- Cervix
Answer : A (Skin of the inner arm above elbow)
Question 31: What is the difference in oral contraceptives and hormonal implants?
- They differ in their sites of implantation
- They differ in their duration of action
- Both A and B
- None of the above
Answer : C ( Both A and B )
Question 32: Tubectomy is a method of sterilisation in which?
- Small part of the Fallopian tube is removed or tied up
- Ovaries are removed surgically
- Small part of vas deferens is removed or tied up
- Uterus is removed surgically
Answer : A (Small part of the Fallopian tube is removed or tied up)
Question 33: Name the part cut and tied in male sterilisation. Also, name the procedure?
- Vas deferens; Tubectory
- Vas deferens; Vasectomy
- Vasa efferentia; Tubectomy
- Vasa efferentia; Vasectomy
Answer : B (Vas deferens; Vasectomy)
Question 34: Which of the following approaches does not give the defined action of contraceptive?
- Intra uterine devices – Increase phagocytosis of sperms, suppress sperm motility and fertilising capacity of sperms
- Hormonal contraceptives – Prevent retard entry of sperms, prevent ovulation and fertilisation
- Vasectomy – Prevents spermatogenesis
- Barrier methods – Prevent fertilisation
Answer : C (Vasectomy – Prevents spermatogenesis)
Question 35: Which of the following birth control measure considered as the safest?
- The rhythm method
- Use of physical barriers
- Termination of unwanted pregnancy
- Sterilisation techniques
Answer : D (Sterilisation techniques)
Question 36: Which of the following is incorrect regarding vasectomy?
- No sperm occurs in seminal fluid
- No sperm occurs in epididymis
- Vasa deferentia is cut and tied
- Irreversible sterility
Answer : B (No sperm occurs in epididymis)
Question 37: MTP stands for?
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy
- Mental Trauma Phase
- Menstrual Pain
- Menstrual Temporary Pain is safe
Answer : A (Medical Termination of Pregnancy)
Question 38: During which phase of the pregnancy MTP
- Ist trimester
- 2nd trimester
- 3rd trimester
- 4th trimester
Answer : A (Ist trimester)
Question 39: MTP is of much risk in which phase of the pregnancy?
- 2nd trimester
- 1st trimester
- 1st week
- 2nd week
Answer : A ( 2nd trimester)
Question 40: MTP helps to overcome pregnancy that result due to?
- Unwanted
- Unsafe sex
- Failure of contracepting
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 41: The other name for STDs are?
- Venereal diseases
- Reproductive tract infections
- Both A and B
- None of the above
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 42: Hepatitis-B and HIV spreads through?
- Sharing needles
- Transfusion of blood
- Infected mother to child
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 43: Which of the following STDs are curable?
- Chlamydia
- Syphilis
- AIDS
- Both A and B
Answer : D ( Both A and B)
Question 44: STDs caused by bacteria include?
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhoea
- Both A and B
- None of these
Answer : C ( Both A and B )
Question 45: Incidents of STD are very high among persons, in the age group of?
- 15 – 35 years
- 15 – 30 years
- 15 – 24 years
- 15 – 45 years
Answer : C (15 – 24 years)
Question 46: One of the legal methods of birth control is?
- Abortion by taking an appropriate medicine
- By abstaining from coitus from day 10 – 17 of the menstrual cycle
- By having coitus at the time of day break
- By a premature ejaculation during coitus
Answer : B ( By abstaining from coitus from day 10 – 17 of the menstrual cycle)
Question 47: Ectopic pregnancies are referred to as?
- Pregnancies with genetic abnormality
- Implantation of embryo at site other than uterus
- Implantation of defective embryo in the uterus
- Pregnancies terminated due to the hormonal imbalance
Answer : B ( Implantation of embryo at site other than uterus )
Question 48: Assisted reproductive technology, IVF involves transfer of?
- Ovum into the Fallopian tube
- Zygote into the Fallopian tube
- Zygote into the uterus
- Embryo with 16 balastomeres into the Fallopian tube
Answer : B (Zygote into the Fallopian tube)
Question 49: IVF in which the early zygote with up to 8 blastomeres is transferred to the Fallopian tube is called?
- ZIFT
- GIFT
- ICSI
- IUI
Answer : A (ZIFT)
Question 50: IVF in which zygote with more than 8 blastomeres is transferred into female body it is called
- IUT
- GIFT
- ZIFT
- ICSI
Answer : A (IUT)
Question 51: The test – tube baby programme employs which one of the following techniques?
- Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
- Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI)
- Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT)
- Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
Answer : Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
Question 52: IUT stands for
- Inter uterine transfer
- Intra Uterine transfer
- In – uterus transfer
- None of these
Answer : B (Intra Uterine transfer)
Question 53: False statement about ZIFT is
- Zygote in the fallopian transfer
- Type of IVF
- Embryo with more than 8 blastomeres are used
- Zygote or embryo with up to 8 blastomeres are used
Answer : C (Embryo with more than 8 blastomeres are used)
Question 54: Difference between ZIFT and IUT lies in the
- Methodology
- Nature of the sperms
- Nature of the cells
- Number of the cells
Answer : D (Number of the cells)
Question 55: Embryo with more than 16 blastomeres formed due to in vitro fertilization is transferred into
- Uterus
- Fallopian tube
- Fimbriae
- Cervix
Answer : A (Uterus)
Question 56: What is false for GIFT ?
- It is Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer
- Ovum is transferred into the oviduct
- Zygote is transferred into Fallopian tube
- Used when the receptive is sterile
Answer : C (Zygote is transferred into Fallopian tube)
Question 57: A childless couple can be assisted to have a child through a technique called GIFT. The fullform of this technique is
- Gamete Inseminated Fallopian Transfer
- Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer
- Gamete Internal Fertilisation and transfer
- Germ Cell Internal Fallopian Transfer
Answer : B (Gamete intra fallopian transfer)
Question 58: ICSI stands for
- In Cytoplasmic Sperm Insemination
- Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection
- Inter Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection
- In Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection
Answer : B ( Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection )
Question 59: Which of the following method is used when male partner is unable to inseminate into the female partner due to the low sperm count?
- AI
- IUI
- Both A and B
- None of the above
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 60: IUI stands for
- Intra Uterine Insemination
- Inter Uterine Insemination
- In Uterine Insemination
- Inner Uterine Insemination
Answer : A (Intra uterine insemination)
Question 61: Increased IMR and decreased MMR population will?
- Cause rapid increase in growth rate
- Result in decline in growth rate
- Not cause significant change in growth rate
- Result in an explosive population
Answer : C (Not cause significant change in growth rate)
Question 62: Condoms are one of the most popular contraceptives because of the following reasons?
- These are effective barriers for insemination
- They do not interfere with coital act
- These help in reducing the risk of STDs
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 63: Which statement is true about diaphragm?
- They are introduced into the uterus
- They are placed to cover the cervical region
- They act as chemical barriers for sperm entry
- They act as spermicidal agents
Answer : B (They are placed to cover the cervical region)
Question 64: Emergency contraceptives are effective if used within 72 hrs of?
- Coitus
- Ovulation
- Menstruation
- Implantation
Answer : A (Coitus)
Question 65: The correct surgical procedure as a contraceptive method is
- Ovariectomy
- Hysterectomy
- Vasectomy
- Castration
Answer : C ( Vasectomy )
Question 66: From the sexually transmitted diseases mentioned below, identify the one which does not specifically affect the sex organs?
- Syphilis
- AIDS
- Gonorrhoea
- Genital warts
Answer : B (AIDS)
MCQ Of Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Question 1: Genetics is the branch of biology which deals with
- Variation
- Inheritance
- Both A and B
- Study of characters
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 2: The tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called
- Variation
- Heredity
- Inheritance
- Resemblance
Answer : B (Heredity)
Question 3: Who is called the father of genetics?
- Hugo de Vries
- Morgan
- Mendel
- Darwin
Answer : C (Mendel)
Question 4: Mendel’s experimental material was
- Pisum sativum
- Lathyrus odoratus
- Oryza sativa
- Mirabilis jalapa
Answer : A (Pisum sativum)
Question 5: How many type of gametes can be produced by a diploid organism that is heterozygous for 3 loci ?
- 6
- 4
- 8
- 3
Answer : C (8)
Question 6: During Mendel’s investigation, it was first time that …A… and …B… were applied in biology. Here A and B refers to
- A-statistical analysis; B-mathematical logic
- A-statistical analysis; B-physical logic
- A-statistical analysis; B-chemistry logic
- A-statistical analysis; B-simple logic
Answer : A (A-statistical analysis; B-mathematical logic )
Question 7: How many pairs of true breeding varieties were selected by Mendel for his experiment on pea plant?
- 12
- 14
- 13
- 15
Answer : B (14)
Question 8: Which type of pollination method was adopted by Mendel in his experiment?
- Artificial
- Cross – pollination
- Natural
- Both A and B
Answer : D (Both A and B)
Question 9: F1 – progeny of a cross between pure tall and dwarf plant is always
- Tall
- Short
- Intermediate
- None of these
Answer : A (Tall)
Question 10: How did Mendel obtained recessive character in F2-generation?
- By self-pollinating F1
- By self-pollinating F2
- By cross-pollinating F1
- By cross-pollinating F2
Answer : A (By self-pollinating F1)
Question 11: Both phenotypic and genotypic ratio are same in F2 generation in
- Co – dominance
- Incomplete dominance
- Out – cross
- More than one option is correct
Answer : D (More than one option is correct)
Question 12: Theoretically in incomplete dominance one allele functions as normal, while another allele may function as
- Normal allele
- Non – functional allele
- Normal but less efficient allele
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 13: Mendel did not propose the theory of
- Dominance
- Incomplete dominance
- Segregation
- Independent assortment
Answer : B (Incomplete dominance)
Question 14: In a red and white flowered cross of mirabilis jalapa F2 generation has red, pink and white flowered plants in the ratio of
- 2 : 1 : 1
- 1 : 1 : 2
- 1 : 2 : 1
- 1 : 0 : 1
Answer : A (2 : 1 : 1)
Question 15: Which mendelian idea is depicted by a cross in which the F1 generation resembles both the parents ?
- Incomplete dominance
- Law of dominance
- Inheritance of one gene
- Codominance
Answer : D (Codominance)
Question 16: The character that is expressed in the F1 – generation is called the
- Recessive character
- Dominant character
- Codominant character
- None of these
Answer : B (Dominant character)
Question 17: If the genotype of an individual consists of only one type of genes at same locus. It is called
- Homozygous
- Heterozygous
- Monoallelic
- Uniallelic
Answer : A (Homozygous)
Question 18: The types of gametes produced by a heterozygous allelic pair are
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Many
Answer : B (2)
Question 19: A cross in which parents differ in a single pair of contrasting character is called
- Monohybrid cross
- Dihybrid cross
- Trihybrid cross
- Tetrahybrid cross
Answer : A (Monohybrid cross)
Question 20: The genotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross in F2 – generation is
- 3 : 1
- 1 : 2 : 1
- 2 : 1 : 1
- 9 : 3 : 3 : 1
Answer : B (1 : 2 : 1)
Question 21: Choose the incorrect pair amongst the following characters Mendel choose for his experiments.
- Pod shape – Elongated/constricted
- Seed colour – Yellow/green
- Seed shape – Round/wrinkled
- Flower position – Axial/terminal
Answer : A (Pod shape – Elongated/constricted )
Question 22: Graphical representation to calculate the probability of all possible genotype of an offspring in genetic cross is called
- Bunett square
- Punnet square
- Morgan square
- Mendel square
Answer : B (Punnet square)
Question 23: Mendel self-pollinated the F2-plant and found that …A… plants continued to generate dwarf plant in …B… and …C… generations. He concluded that the genotype of the dwarfs is …D…
Choose the correct option for A, B, C and D.
- A – dwarf, B – F3, C – F4, D – homozygous
- A – dwarf, B – F3, C – F4, D – heterogygous
- A – tall, B – F5, C – F6, D – homozygous
- A – tall, B – F5, C – F6, D – heterozygous
Answer : A (A – dwarf, B – F3, C – F4, D – homozygous )
Question 24: Test cross is
- Recessive F1 – plant crosses with dominant F2-plant
- Recessive F2 – plant crosses with dominant
- F3 – plant
- Dominant F1 – plant crosses with recessive parent plants
- Dominant F2 – plant crosses with heterozygous parent plants
Answer : D (Dominant F1 – plant crosses with recessive parent plants )
Question 25: The allele which expresses itself in both homozygous and heterozygous condition is called
- Dominant allele
- Recessive allele
- Incomplete dominant allele
- Split allele
Answer : A (Dominant allele)
Question 26: Mendel’s principle of segregation means that the germ cells always receive
- One pair to alleles
- One quarter of the genes
- Either one allele of father or one allele of mother
- Any pair of alleles
Answer : C (Either one allele of father or one allele of mother)
Question 27: Law based on fact that the characters don’t show any blending and both the characters are recovered as such in F2 – generation although one character was absent in F1 – progeny, is
- Law of purity of gametes
- Law of independent assortment
- Law of incomplete dominance
- Law of dominance
Answer : A (Law of purity of gametes)
Question 28: The ABO blood group are controlled by
- I – gene
- c – gene
- B – gene
- n – gene
Answer : A (I – gene)
Question 29: When there are more than two allele controlling the same character. These are called
- Many alleles
- Polyalleles
- Multiple alleles
- All of these
Answer : C (Multiple alleles)
Question 30: Mother = A blood group
Father = AB blood group
The child will not have
- A blood group
- O blood group
- B blood group
- AB blood group
Answer : B (O blood group)
Question 31: Starch synthesis gene in pea plant in heterogygous condition produces starch grain of intermediate size this shows
- Complete dominance
- Incomplete dominance
- Codominance
- None of these
Answer : B (Incomplete dominance)
Question 32: The types of gametes formed by the genotype RrYy are
- RY, Ry, rY, ry
- RY, Ry, ry, ry
- Ry, Ry, Yy, ry
- Rr, RR, Yy, YY
Answer : A (RY, Ry, rY, ry)
Question 33: Which process was used to study the independent assortment ?
- Monohybrid cross
- Dihybrid cross
- Trihybrid cross
- Tetrahybrid cross
Answer : B (Dihybrid cross)
Question 34: Ratio observed in dihybrid cross (phenotypically)
- 3 : 1
- 1 : 2 : 1
- 9 : 7
- 9 : 3 : 3 : 1
Answer : D (9 : 3 : 3 : 1)
Question 35: Multiple alleles control the character of
- Only skin colour
- Only blood group
- Blood groups and skin colour
- Sickle cell
Answer : B (Only blood group)
Question 36: Who proposed the chromosomal theory of inheritance ?
- Sutton and Mendel
- Boveri and Morgan
- Morgan and Mendel
- Sutton and Boveri
Answer : D (Sutton and Boveri )
Question 37: Morgan worked with any fruit fly named as
- Drosophila melanogaster
- Magnifiera Indica
- Mirabilis jalapa
- Drosophila Indica
Answer : A (Drosophila melanogaster)
Question 38: Linked gene is related to …A… And an linked gene is related to …B…
Choose correct option for A and B
- A – linkage; B – crossing over
- A – crossing over; B – linkage
- A – crossing over; B – recombination
- A – recombination; B – crossing gene
Answer : A (A – linkage; B – crossing over)
Question 39: How many linkage groups are present in human male ?
- 24
- 23
- 46
- 22
Answer : A (24)
Question 40: In which state crossing over takes place ?
- Leptotene
- Cytokinesis
- Pachytene
- Diakinesis
Answer : C (Pachytene)
Question 41: Linkage reduce the frequency of
- Hybrids
- All parental types
- Homozygous recessive parents
- Heterozygous recessive parents
Answer : A (Hybrids)
Question 42: Experimental evidences of chromosomal theory of inheritance was given by
- HT Morgan
- TH Morgan
- Hugo de Vries
- De Vries
Answer : B (TH Morgan)
Question 43: Linkage groups are always present on the
- Homologous chromosomes
- Analogous chromosomes
- Sex chromosomes
- Heterologous chromosomes
Answer : A (Homologous chromosomes)
Question 44: Which of the following statement is not true of two genes that show 50% recombination frequency ?
- The genes may be on different chromosomes
- The genes are tightly linked
- The genes show independent assortment
- If the genes are present on the same chromosome, they undergo more than one crossovers in every meiosis
Answer : B (The genes are tightly linked)
Question 45: Choose the incorrect pair with respect to sex determination in different organisms.
- Grasshopper = XO type
- Birds = ZZ – ZW type
- Drosophila = XX – XO type
- Human = XX – XY type
Answer : C (Drosophila = XX – XO type)
Question 46: Sickle – cell anemia is classical example of
- Frame shift mutation
- Point mutation
- Both A and B
- None of the above
Answer : B (Point mutation)
Question 47: A normal-visioned man whose father was colour blind, marries a woman whose father was also colour blind, They have their first child as a daughter. What are the chances that this child would be colour blind?
- 100%
- 0%
- 25%
- 50%
Answer : B (0%)
Question 48: Which of the following most appropriately describes haemophilia?
- X-linked recessive gene disorder
- Chromosomal disorder
- Dominant gene disorder
- Recessive gene disorder
Answer: A (X-linked recessive gene disorder)
Question 49: Substitution of valine at 6th position of beta globin chain of haemoglobin results in individuals suffering from
- Haemophilia
- Phenylketonuria
- Sickle-cell anaemia
- Down’s syndrome
Answer : C (Sickle cell anaemia)
Question 50: In haemophilia, a single protein that is a part of cascade of protein involved in …A… of…B… is affected. Single cut will result in …C… bleeding.
Choose the correct option for A, B and C.
- A – coagulation, B – RBC, C – continuous
- A – coagulation, B – WBC, C – continuous
- A – clotting, B – blood, C – continuous
- A – coagulation, B – blood, C – continuous
Answer : C (A – clotting, B – blood, C – continuous)
Question 51: The enzyme missing in phenylketonuria is
- Phenylalanine hydroxylase
- Phenylalanine reductase
- Phenylalanine oxidase
- Phenylalanine oxidoreductase
Answer : A (Phenylalanine hydroxylase )
Question 52: In sickle – cell anaemia, GAG is replaced by
- GGA
- GUG
- AAG
- GGG
Answer : B (GUG)
Question 53: Phenylalanine does not changed to tyrosine. This condition is seen in
- Sickle-cell anaemia
- Phenylketonuria
- Thalassaemia
- Haemophilia
Answer : B (Phenylketonuria)
Question 54: Choose the incorrect pair.
- Down’s syndrome – Extra copy of chromosome no. 21
- Turner’s syndrome – Loss of an X – chromosome in females
- Polyploidy – Seen in plants
- None of the above
Answer : D (None of the above)
Question 55: In phenylketonuria, the phenylalanine gets converted to
- Acetic acid
- Phenyl acetic acid
- Phenyl pyruvic acid
- Pyruvic acid
Answer : C (Phenyl pyruvic acid)
Question 56: Klinefelter’s syndrome results from
- XX egg and Y from sperm
- XX egg and XY sperm
- X egg and YY sperm
- XY egg and X sperm
Answer : A (XX egg and Y from sperm)
Question 57: Phenylketonuria disease is
- Autosomal dominant
- Autosomal recessive
- Sex-linked recessive
- Sex-linked dominant
Answer : B (Autosomal recessive )
Question 58: Pick out the correct statements.
I. Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disease.
II. Down’s syndrome is due to aneuploidy.
III. Phenylketonuria is an autosomal recessive gene disorder.
IV. Sickle-cell anaemia is an X-linked recessive disorder.
- II and IV
- I, II and III
- I, III and IV
- I and IV
Answer : B (I, II and III)
Question 59: Which of the following are Mendelian disorder?
- Thalassemia
- Cystic fibrosis
- Phenylketonuria
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 60: In a dihybrid cross, if you get 9:3:3:1 ratio it denotes that
- The alleles of two genes are interacting with each other
- It is a multigenic inheritance
- It is a case of multiple allelism
- The alleles of two genes are segregating independently
Answer : D (The alleles of two genes are segregating independently)
Question 61: Which of the following will not result in variation among siblings ?
- Independent assortment of genes
- Crossing over
- Linkage
- Mutation
Answer : C (Linkage)
Question 62: Which of the following is not a dominant trait ?
I Colour blindness
II Rh factor
III Albinism
IV Haemophilia
- I , III , IV
- I , II , III , IV
- II , III , IV
- I , II , III
Answer : A ( I , III , IV)
Question 63: Polyploidy wheat does not normally show and increase in
- Size
- Vigour
- Resistance to disease
- Length of life cycle
Answer : D (Length of life cycle)
Question 64: Distance between the genes and percentage of recombination shows
- A direct relationship
- An inverse relationship
- A parallel relationship
- No relationship
Answer : A (A direct relationship)
Question 65: ZZ / ZW type of sex determination is seen in
- Platypus
- Snails
- Cockroach
- Peacock
Answer : D (Peacock)
Question 66: If a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male progeny, the disease is
- Autosomal dominant
- Autosomal recessive
- Sex – linked dominant
- Sex – linked recessive
Answer : D (Sex – linked recessive)
MCQ Of Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question 1: The length of DNA usually depends on nucleotides
- Position of nucleotides
- Number of nucleotides
- Both A and B
- None of the above
Answer : B (Number of nucleotides)
Question 2: Haploid content of human DNA has
- 3.3 × 10⁷ bp
- 3.3 × 10⁸ bp
- 3.3 × 10⁹ bp
- 3.3 × 10¹⁰ bp
Answer : C (3.3 × 10⁹ bp)
Question 3: Nitrogenous bases are linked to sugar by
- Hydrogen bond
- phosphodiester bond
- N – glycosidic bond
- O – glycosidic bond
Answer : C (N – glycosidic bond)
Question 4: What is the difference between adenosine and deoxyadenosine?
- Only sugar
- Only purine
- Only phosphate
- All of these
Answer : A (Only sugar)
Question 5: When a phosphate group is linked to …A… group of nucleoside through …B… bond, a corresponding …C… is formed.
Choose the correct option for A, B and C.
- A – 5′ OH, B – phosphodiester bond, C – nucleotide
- A – 3′ OH, B – phosphodiester bond, C – nucleotide
- A – 2′ OH, B – phosphodiester bond, C – nucleotide
- A – 5 OH, B – phosphodiester bond, C – nucleoside
Answer : A (A – 5′ OH, B – phosphodiester bond, C – nucleotide )
Question 6: Backbone of DNA is formed by
- Sugar
- Phosphates
- Both A and B
- Nitrogenous bases (purine and pyrimidine)
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 7: Which additional group is present at the 2′ position of the ribose sugar in RNA ?
- R—H
- CHO
- OH
- COOH
Answer : C (OH)
Question 8: In some viruses, the flow of information is in reverse direction, i.e. from RNA to DNA. Can you suggest a simple name to the process?
- Transcription
- Transception
- Reverse transcription
- Translation
Answer : C (Reverse transcription)
Question 9: Find out the number of base pairs in in E. coli DNA if its DNA is 1.36 mm long.
- 4 × 10⁶ bp
- 3 × 10⁶ bp
- 2 × 10⁶ bp
- 7 × 10⁶ bp
Answer : A (4 × 10⁶ bp)
Question 10: Positively charged basic proteins that are found in eukaryotes are called
- Histones
- Protamine
- Arginine
- Lysine
Answer : A (Histones)
Question 11: In the given diagram, identify A, B and C.
- A – DNA, B – Histone, C – Histone octamer
- A – RNA, B – Histone, C – Histone octamer
- A – DNA, B – Histone, C – Histone tetramer
- A – RNA, B – Histone, C – Histone tetramer
Answer : A (A – DNA, B – Histone, C – Histone octamer)
Question 12: Lightly stained part of chromatin which remains loosely packed and its transcriptionally active named as
- Euchromatin
- Heterochromatin
- Chromatosome
- Chromonemata
Answer : A (Euchromatin)
Question 13: Experiment organism of Frederick and Griffith was
- Variola virus
- Tuberculosis bacteria
- Actinomycetes
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
Answer : D (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
Question 14: In Griffith’s experiment, mice infected with the …A… die from pneumonia infection but mice infected with …B… don’t develop pneumonia. Choose the correct option for A and B.
- A – S strain; B – S + R strain
- A – S strain; B – R strain
- A – R strain; B – S strain
- A – R strain; B – S + R strain
Answer : B (A – S strain; B – R strain)
Question 15: A molecule that can act as a genetic material must fulfill the traits given below, except
- It should be able to express itself in the form of ‘Mendelian characters’
- It should be able to generate its replica
- It should be unstable structurally and chemically
- It should provide the scope for slow changes that are required for evolution
Answer : C (It should be unstable structurally and chemically)
Question 16: In Hershey and Chase experiment, Bacteriophage nucleic acids were labelled as
- ³²P labelled phosphate
- ³H labelled H2O
- ³⁵S labelled sulphate
- ¹⁴C labelled CO2
Answer : A (³²P labelled phosphate)
Question 17: Hershey and Chase concluded that viral infecting agent in their experiment was
- Protein
- DNA
- RNA
- Both B and C
Answer : B (DNA)
Question 17: RNA is the genetic material in
- All bacteria
- Tobacco Mosaic Viruses (TMV)
- QB bacteriophage
- Both B and C
Answer : D (Both B and C)
Question 18: Which group present in RNA nucleotide is very reactive and makes RNA liable and easily degradable than DNA?
- 3-OH’ group at every nucleotide
- 2-OH group on ribose sugar
- 3-OH’ group on ribose sugar
- 4 OH’ group on ribose sugar
Answer : B (2-OH group on ribose sugar)
Question 19: Stability of DNA is impacted by to
- Deoxyribose sugar
- Presence of thymine in place of uracil
- Both A and B
- None of the above
Answer : C (Both A and B)
Question 20: Which one of the following is not applicable to RNA ?
- Complementary base pairing
- 5′ phosphoryl and 3′ hydroxyl ends
- Heterocyclic nitrogenous bases
- Chargaff’s rule
Answer : D (Chargaff’s rule)
Question 21: DNA replication is semiconservative. It was first shown in
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Vicia faba
- Algae
Answer : B (Bacteria)
Question 22: Name the heavy isotope used by Meselson and Stahl for proving the semiconservative mode of DNA.
- ¹⁵NH4Cl
- ¹⁴NH3Cl2
- ¹³NH2Cl3
- All of these
Answer : A (¹⁵NH4Cl)
Question 23: Heavy DNA can be differentiated from normal DNA by which centrifugation technique?
- AgCl density gradient
- CaSO4 density gradient
- CsCl density gradient
- KCl density gradient
Answer : C ( CsCl density gradient)
Question 24: In Meselson and Stahl’s experiment, DNA extracted from the culture one generation after the transfer from ¹⁵N to ¹⁴N medium had a hybrid (or intermediate density). Why?
- Because the generation time of E. coli (culture) was about 20 minutes
- Because it would take 20 minutes for RNA replication
- Because it would take 20 minutes for replication of DNA to RNA (transcription)
- Because it would take 20 minutes for translation RNA to protein
Answer : A (Because the generation time of E. coli (culture) was about 20 minutes)
Question 25: Radioisotope used by Taylor in his experiment was
- Iron
- Titanium
- Thymidine
- Copper
Answer : C (Thymidine)
Question 26: DNA polymerase is
- DNA dependent
- DNA independent
- RNA dependent
- RNA independent
Answer : A (DNA dependent)
Question 27: DNA dependent RNA polymerase catalyses transcription on one strand of the DNA which is called the
- Template strand
- Coding strand
- Alpha strand
- Anti – strand
Answer : A (Template strand )
Question 28: DNA dependent DNA polymerases catalyses polymerization in which direction ?
- 3′ — 5′
- 5′ — 2′
- 5′ — 3′
- 2′ — 5′
Answer : C (5′ — 3′)
Question 29: Which among the following statements does not stands true for DNA replication ?
- Replication initiate randomly at any place in DNA by DNA polymerase
- In eukaryotes, DNA replication takes place at S – phase of cell cycle
- Failure of cell division after DNA replication results in polyploidy
- E.coli.having 4.6 × 10⁶ base pair completes DNA replication within 38 minutes
Answer : A (Replication initiate randomly at any place in DNA by DNA polymerase)
Question 30: On which strand of DNA, replication is continuous ?
- 5′ — 3′ polarity strand
- 3′ — 5′ polarity strand
- 3′ — 2′ polarity strand
- 3′ — 4′ polarity strand
Answer : B (3′ — 5′ polarity strand)
Question 31: Identify A, B and C strands.
- A – Continuous strand, B – Discontinuous strand, C – Template strand
- A – Leading strand, B – Lagging strand, C – Parental strand
- A – 5′ — 3′ strand B, 3 – 5′ strand, C – Parental strand
- All of the above
Answer : A (A – Continuous strand, B – Discontinuous strand, C – Template strand)
Question 32: Why both the strands of DNA are not copied during transcription?
- Because RNA molecule with different sequences will be formed
- Because RNA molecule with same sequences will be formed
- Because RNA molecule with identical sequences will be formed
- Because DNA molecule with different sequences will be formed
Answer : A (Because RNA molecule with different sequences will be formed)
Question 33: The strand which do not code for anything is called
- Coding strand
- Non – coding strand
- Template strand
- Antisense strand
Answer : A (Coding strand )
Question 34: If the coding strand has the sequence
5′ — ATCGATCG — 3′
then find out the sequence of non – coding strand.
- 3′ — TAGCTAGC — 5′
- 5′ — TACGTACG — 3′
- 5′ —UAGGUACG — 3′
- 5′ — UACFUACG — 3′
Answer : A (3′ — TAGCTAGC — 5′)
Question 35: Identify the correct pair of mRNA type and its function.
- Messanger RNA — Provides the template
- Transfer RNA — brings amino acids and reads genetic code
- Ribosomal RNA — Plays catalytic role during translation
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 36: In bacteria, which enzyme catalyses the transcription of all types of RNA (mRNA, RNA and rRNA)?
- DNA dependent RNA polymerase
- DNA dependent DNA polymerase
- RNA dependent RNA polymerase
- RNA dependent DNA polymerase
Answer : A (DNA dependent RNA polymerase)
Question 37: Splicing is the removal of
- Introns and exons are joined
- Exons end introns are joined
- Exons only
- Exons and introns
Answer : A (Introns and exons are joined)
Question 38: The diagram shows an important concept in the genetic implication of DNA. Fill in the blanks A to C.
- A – transcription, B – replication, C – James Watson
- A – translation, B – transcription, C – Erwin Chargaff
- A – transcription, B – translation, C – Francis Crick
- A – translation, B – extension, C – Rosalind Franklin
Answer : C ( A – transcription, B – translation, C – Francis Crick)
Question 39: Who developed the technique of synthesizing RNA molecules with well defined combination of bases to develop genetic code?
- Crick et. al
- Har Gobind khorana
- Matthaei
- Nirenberg
Answer: : B (Har Gobind khorana)
Question 40: The one aspect, which is not a salient feature of genetic code is, its being
- Degenerate
- Ambiguous
- Universal
- Specific
Answer : B (Ambiguous)
Question 41: Codons are unambiguous, means one codon code for
- More than one amino acid
- Two amino acids
- Only one amino acid
- Non-sense amino acid
Answer : C (Only one amino acid)
Question 42: The codon AUG codes for (in eukaryotes)
- Methionine
- Histidine
- Tryptophan
- Alanine
Answer : A (Methionine)
Question 43: Identify the stop codons in given options.
- UAA, UAG, UGA
- UCA, UCC, UCA
- UGC, UCG, UCC
- UUU, UAT, UTA
Answer : A (UAA, UAG, UGA)
Question 44: Which mutation of the genetic bases gives the proof that codon is triplet and reads in a contagious manner?
- Frameshift mutation
- Point mutation
- Both A and B
- Inversion mutation
Answer : A (Frameshift mutation)
Question 45: tRNA is a compact molecule which looks like
- M – shaped
- P – shaped
- L – shaped
- K – shaped
Answer : C (L – shaped)
Question 46: Which enzyme will be produced in a cell in which there is a non – sense mutation in the lac Y – gene ?
- B – galactosidase
- Lactose permease
- Transacetylase
- Lactose permease and transacetylase
Answer : A (B – galactosidase)
Question 47: The accessibility of the promoter regions of prokaryotic DNA is (in many cases) regulated by the interaction of proteins with the sequences termed as
- Regulator
- Promoter
- Operator
- Structural genes
Answer : C (Operator)
Question 48: An operon is considered to regulate a unit
- Translational unit
- Genetic unit
- Protein unit
- Enzymatic unit
Answer : B (Genetic unit)
Question 49: Gene regulation governing lactose operon of E.coli the lac I gene products is
- Positive and inducible because it can be induced by lactose
- Negative and inducible because it repressor protein prevents transcription
- Negative and repressible because repressor proteins prevents transcription
- Feedback inhibition because excess of B – galactosidase can switch off transcription
Answer : B (Negative and inducible because it repressor protein prevents transcription)
Question 50: Lactose is transported into cells through
- B-galactosidase
- Permease
- Transacetylase
- Transferase
Answer : B (Permease)
Question 51: Given the diagram of the lac operon showing an operon of inducible enzymes. Identify components and enzymes (A, B, C, D and E).
- A – Galactosidase, B – Permease, C – Transacetylase, D – Repressor protein, E – Inducer (lactose)
- A – Galactosidase, B – Permease, C – Transacetylase, D – Inducer (lactose), E – Repressor protein
- A – Galactosidase, B – Transacetylase, C – Permease, D – Repressor protein, E – Inducer (lactose)
- A – Permease, B – Transacetylase, C – Galactosidase, D – Repressor protein, E – Inducer (lactose)
Answer : A (A – Galactosidase, B – Permease, C – Transacetylase, D – Repressor protein, E – Inducer (lactose))
Question 52: Repressor proteins of lac operon binds to
- Exons
- Introns
- Operator
- Structural genes
Answer : C (Operator)
Question 53: Why glucose and galactose cannot act as an inducer for lac operon ?
- Because they cannot bind with the repressor
- Because they can bind with the repressor
- Because they can bind with the operator
- Because they can bind with the regulator
Answer : A (Because they cannot bind with the repressor)
Question 54: Identify the statement not concerned with human genome project.
- It was completed in 2003
- It aims to determine the sequence of 3 billion chemical base pairs and store it in data bases
- It associated ethical legal and social issues arising from the project
- It is not associated with non-human organisms DNA sequences
Answer : D (It is not associated with non-human organisms DNA sequences)
Question 55: How genetic and physical maps were generated in HGP?
- By using DNase
- By using RNase
- By using restriction endonuclease
- By using automated DNA sequences
Answer : C (By using restriction endonuclease )
Question 56: SNP-Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms is
- Location on RNA where the single base differs
- Location on proteins where the single base differs
- Location on genome where the single base of DNA differs
- Location on genome where many bases of DNA differs
Answer : C (Location on genome where the single base of DNA differs)
Question 57: SNPs can be used for
- Finding chromosome locations for disease associated sequences
- Tracing human history
- Evolution
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 58: Satellite DNA or repetitive DNA
- Do not code for any protein
- Forms a large portion of human genome
- Shows high degree of polymorphism
- All of the above
Answer : D (All of the above)
Question 59: VNTR belongs to the class of satellite DNA referred to as
- Microsatellite DNA
- Minisatellite DNA
- Megasatellite DNA
- Repititive DNA
Answer : B (Minisatellite DNA)
Question 60: Steps in DNA fingerprinting are
Isolation of DNA
↓
Digestion of DNA by (A)
↓
Separation of DNA by (B)
↓
Transfering of DNA to (C)
↓
DNA hybridisation using (D)
↓
Detecting of hybridised DNA by (E)
Complete the accompanying flowchart. A, B, C, D and E in the flowchart are
- A – Restriction endonuclease, B – Electrophoresis, C – Nitrocellulose or nylon, D – Labelled VNTR probe, E – Autoradiography
- A – Electrophoresis, B – Restriction endonuclease, C – Nitrocellulose or nylon, D – Labelled VNTR probe, E – Autoradiography
- A – Restriction endonuclease, B – Electrophoresis, C – Labelled VNTR probe, D – Nitrocellulose or nylon, E – Autoradiography ,
- A – Restriction endonuclease, B – Electrophoresis C – Nitrocellulose or nylon, D – Autoradiography, E – Labelled VNTR probe
Answer : A (A – Restriction endonuclease, B – Electrophoresis, C – Nitrocellulose or nylon, D – Labelled VNTR probe, E – Autoradiography)
Question 61: While analysing the DNA of an organism a total number of 5386 nucleotides were found out of which the proportion of different bases were Adenine = 29%, Guanine = 17%, Cytosine = 32%, Thymine = 17%. Considering the Chargaffs rule it can be concluded that
- It is a double-stranded circular DNA
- It is single-stranded DNA
- It is a double-stranded linear DNA
- No conclusion can be drawn
Answer : B (It is single-stranded DNA)
Question 62: The first genetic material could be
- Protein
- Carbohydrates
- DNA
- RNA
Answer : D (RNA)
Question 63: DNA is a polymer of nucleotides which are linked to each other by 3 – 5′ phosphodiester bond. To prevent polymerisation of nucleotides, which of the following modifications would you choose?
- Replace purine with pyrimindines
- Remove/Replace 3′ OH group in deoxyribose
- Remove/Replace 2′ OH group with some other group in deoxyribose
- Both B and C
Answer : B ( Remove/Replace 3′ OH group in deoxyribose)
Question 64: Which one of the following steps in transcription is catalysed by RNA polymerase?
- Initiation
- Elongation
- Termination
- All of these
Answer : C (Termination)
Question 65: With regard to mature mRNA in eukaryotes
- Exons and introns do not appear in the mature RNA
- Exons appear but introns do not appear in the mature RNA
- Introns appear but exons do not appear in the mature RNA
- Both exons and introns appear in the mature RNA
Answer : B (Exons appear but introns do not appear in the mature RNA)
Question 66: The amino acid attaches to the tRNA at its
- 5′ – end
- 3′ – end
- Anticodon site
- DHU loop
Answer : B (3′ – end)
Question 67: In E. coli, the lac operon gets switched on when
- Lactose is present and it binds to the repressor
- Repressor binds to operator
- RNA polymerase binds to the operator
- Lactose is present and it binds to RNA polymerase
Answer : A (Lactose is present and it binds to the repressor)
Question 68: Regulatory proteins are the accessory proteins that interact with RNA polymerase and affect its role in transcription. Which of the following statements is correct about regulatory protein?
- They only increase expression
- They only decrease expression
- They interact with RNA polymerase but do not affect the expression
- They can act both as activators and as repressors
Answer : D (They can act both as activators and as repressors)
Question 69: Which was the last human chromosome to be completely sequenced?
- Chromosome 1
- Chromosome 11
- Chromosome 21
- Chromosome – X
Answer : A (Chromosome 1)
Question 70: The human chromosome with the highest and least number of genes in them are respectively
- Chromosome 21 and Y
- Chromosome 1 and X
- Chromosome 1 and Y
- Chromosome X and Y
Answer : C (Chromosome 1 and Y)
We would love your reading of MCQs for CUET 2022 of other subjects which are as follow.
- Physical Education
- Hindustani Music Vocal
- Political Science
- Geography
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Chemistry
- Economics
- Physics
# MCQ of Biology CUET Class 12
# MCQ of Biology CUET With Answers
# MCQ of Biology CUET 2022
# MCQ of Biology CUET 2023
# MCQ of Biology CUET July Exam
# MCQ of Biology CUET Common University Entrance Exam
Do share this post if you liked the MCQ of Biology CUET Class 12. For more updates, keep logging on BrainyLads