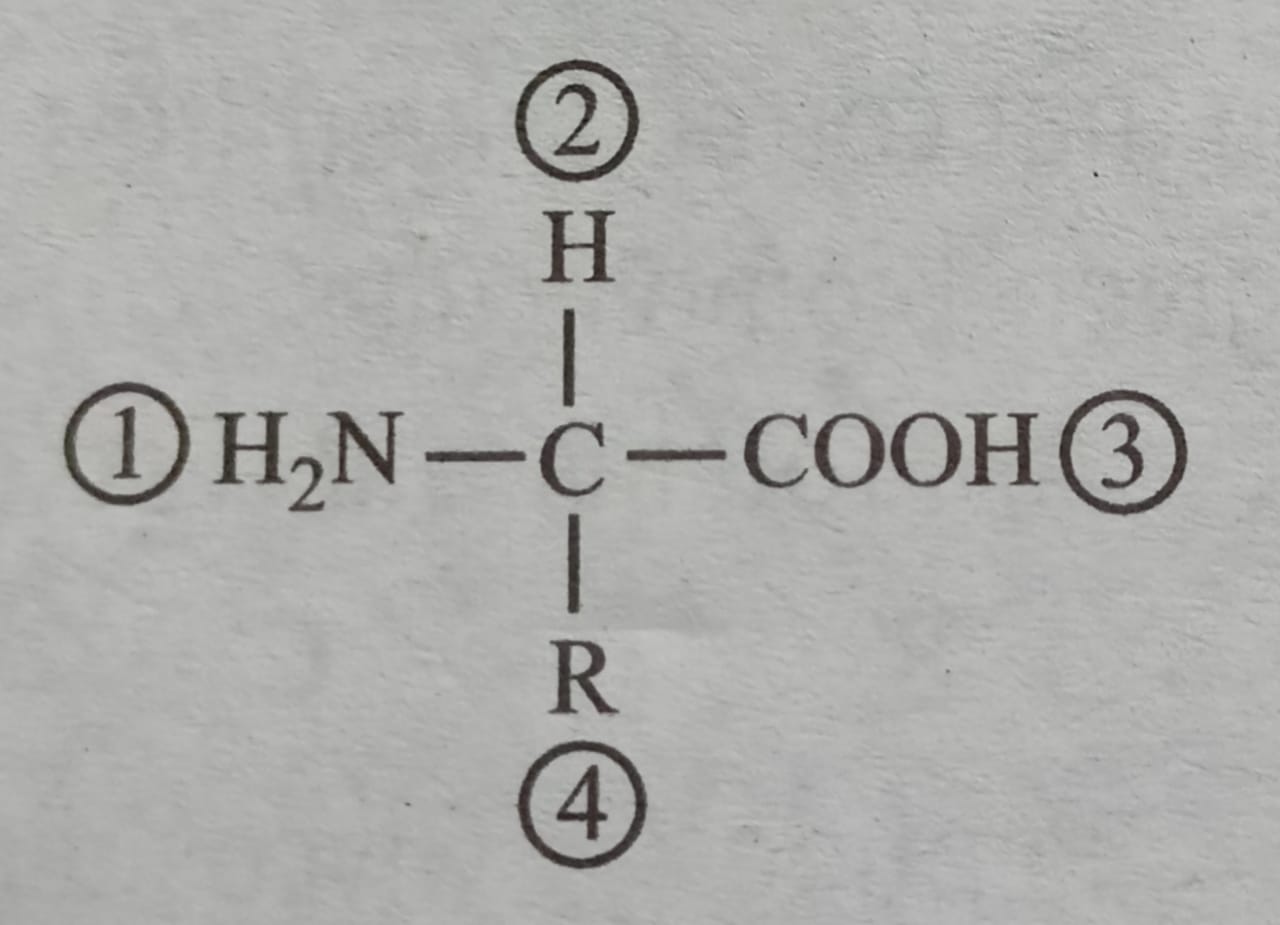MCQ of Biomolecules Class 11 | Chapter 9 | Biology | CBSE
MCQ Of Biomolecules Class 11, Chapter 9, Class 11, Biology
Multiple Choice Questions of Biomolecules, Chapter 9, Class 11, Biology
Question 1: Which of the following is a saturated fatty acid?
- Oleic acid
- Linoleic acid
- Arachidonic acid
- Palmitic acid
Answer : D (Palmitic acid)
Question 2: Study the given statements and select the correct option
(i) Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and lipids are primary metabolites.
(ii) Alkaloids, flavonoids, rubber, etc. are secondary metabolites.
(iii) Linoleic, linolenic and palmitic acids are the three essential fatty acids.
- Statements (i) and (ii) are correct
- Statements (i) and (iii) are incorrect
- Statements (i) and (iii) are correct
- Only statement (ii) is incorrect
Answer : A (Statements (i) and (ii) are correct)
Question 3: Essential amino acids include
- Leucine
- Valine
- Tryptophan
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 4: The component present in both nucleotides and nucleosides is
- Sugar
- Phosphate
- Nitrogenous base
- Both A and C
Answer : D (Both A and C)
Question 5: Saturated fatty acids possess _____bonds between carbon atoms and are _____at room temperature.
- Single, solids
- Double, solids
- Single, liquids
- Double, liquids
Answer : A (Single, solids)
Question 6: Cytidine is a
- Nitrogenous base
- Nucleoside
- Nucleotide
- Nucleic acid
Answer : B (Nucleoside)
Question 7: Lecithin is a
- Sterol
- Glycolipid
- Phospholipid
- Sphingolipid
Answer : C (Phospholipid)
Question 8: Which of the following statements about amino acids is incorrect?
- Essential amino acids are not synthesized in the body, therefore have to be provided in the diet.
- Leucine, isoleucine, lysine, valine are essential amino acids.
- Cysteine and methionine are sulphur containing amino acids.
- Lysine and arginine are acidic amino acids.
Answer : D (Lysine and arginine are acidic amino acids)
Question 9: The inorganic compounds like sulphate, phosphate, etc., are found in
- Acid soluble pool
- Acid insoluble fraction
- Both A and B
- None of these
Answer : A (Acid soluble pool)
Question 10: The four elements called “big – four” which make up 95% of all elements found in a living system are
- C, H, O, N
- C, H, O, P
- C, H, O, S
- C, N, O, P
Answer : A (C, H, O, N)
You may also read MCQ of The Living World, MCQ of Biological Classification, MCQ of Plant Kingdom, MCQ of Animal Kingdom, MCQ of Morphology of Flowering Plants, MCQ of Structural Organization in Animals, MCQ of Cell: The Unit of Life for better understanding of the chapters.
Question 11: The sum total composition of acid soluble and acid insoluble fraction represents the entire composition of
- Dead cells
- Gene pool
- Cellular pool
- Gene library
Answer : C (Cellular pool)
Question 12: Biomolecules are
- Inorganic materials
- Organic materials
- All the carbon compounds obtained from living tissues
- Only DNA and RNA
Answer : C (All the carbon compounds obtained from living tissues)
Question 13: Which of the two groups of the given formula is involved in peptide bond formation between different amino acids?
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
Answer : B (1 and 3)
Question 14: An example of aromatic amino acid is
- Tyrosine
- Phenylalanine
- Tryptophan
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 15: The 20 different amino acids have different
- R – groups
- Carboxylic groups
- Peptide bonds
- Amino groups
Answer : A (R – groups)
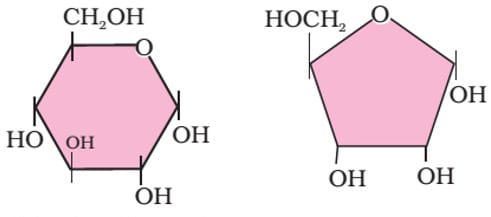
Question 16: Which of the following options correctly identifies the structural formula shown in figure.
A B
- Fructose Ribose
- Glucose Deoxyribose
- Glucose Ribose
- Glucose Fructose
Answer : C (Glucose Ribose)
Question 17: Refer the given reactions.
(i) Adenine + X Adenosine
(ii) Adenosine + Y Adenylic acid
What does X and Y represent here ?
X Y
- Phosphate group Sugar molecule
- Sugar molecule Phosphate group
- Sugar molecule Nitrogenous base
- Nitrogenous base Sugar molecule
Answer : B (Sugar molecule Phosphate group)
Question 18: Acidic amino acids have two –COOH groups and one –NH2 group per molecule. Select the pair that consists of acidic amino acids.
- Aspartic acid, glutamic acid
- Lysine, arginine
- Glycine, alanine
- Both A and B
Answer : A (Aspartic acid, glutamic acid)
Question 19: Adenosine, guanosine, thymidine, uridine, cytidine are all _____ but butadenylicacid, guanylicacid, uridylicacid, cytidylic acid are _____ .
- Nucleotides, nucleosides
- Nucleosides, nucleotides
- Nucleotides, nucleic acids
- Nucleosides, nucleic acids
Answer : B (Nucleosides, nucleotides)
Question 20: Biological molecules are primarily joined by
- Peptide bonds
- Ionic bonds
- Hydrogen bonds
- Covalent bonds
Answer : D (Covalent bonds)
Question 21: How many carbon atoms are generally used in composition of monosaccharides?
- 3 to 7
- 1 to 5
- 5 to 10
- 5 to 15
Answer : A (3 to 7)
Question 22: Take a living tissue, grind it in trichloroacetic acid using pestle and mortar, and then strain it, you would obtain two fractions: acid – soluble and acid – insoluble fraction. Acidinsoluble fraction does not contains
- Polysaccharides
- Nucleic acids
- Lipids
- Flavonoids and alkaloids
Answer : D (Flavonoids and alkaloids)
Question 23: Which of the following is a heteropolymer?
- Cellulose
- Peptidoglycon
- Starch
- Glycogen
Answer : B (Peptidoglycon)
Question 24: In a DNA molecule, the phosphate group is attached to ______ carbon of the sugar residue of its own nucleotide and ______carbon of the sugar residue of the next nucleotide by _____ bonds.
- 5′, 3′, phosphodiester
- 5′, 3′, glycosidic
- 3′, 5′, phosphodiester
- 3′,5′, glycosidic
Answer : A (5′, 3′, phosphodiester)
Question 25: Which of the following statements is not correct regarding chitin?
- It is a storage polysaccharide.
- It is a homopolysaccharide.
- It is a constituent of arthropod exoskeleton and fungal cell wall.
- It is the second most abundant carbohydrate on earth.
Answer : A (It is a storage polysaccharide)
Question 26: The β – pleated sheet structure of proteins is due to
- Formation of peptide bonds
- Coiling of polypeptide chains
- Folding of the coiled polypeptide chains
- Linking together of two or more polypeptide chains
Answer : D (Linking together of two or more polypeptide chains)
Question 27: Primary structure of proteins is due to the presence of
- Peptide bonds
- Disulphide (S – S) linkages
- Hydrogen bonds
- Ionic bonds
Answer : D (Peptide bonds)
Question 28: Read the given statements and select the correct option.
STATEMENT 1 : Haemoglobin is an example of quaternary structure of proteins.
STATEMENT 2: Haemoglobin molecule is composed of four polypeptide chains – two α-chains and two ß-chains.
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Answer : A (Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1)
Question 29: Match Column – I with Column – ll and select the correct option from the codes given below.
| Column – I | Column -II |
| a Galactose | (i) Protein E |
| b Anticoagulant | (ii) Phospholipid |
| c Fructose | (iii) Brain sugar |
| d Lecithin | (iv) Heparin B |
| e Insulin | (v) Fruit sugar |
- a – (v), b – (iii), c – (ii), d – (i), e – (iv)
- a – (v), b – (iii), c – (i), d – (iv), e – (ii)
- a – (i), b – (ii), c – (iii), d – (v), e – (iv)
- a – (iii), b – (iv), c – (v), d – (ii), e – (i)
Answer : D ( a – (iii), b – (iv), c – (v), d – (ii), e – (i))
Question 30: _______ is the most abundant protein in animal world and _______ is the most abundant protein in the whole biosphere.
- Collagen, RuBisCO
- Collagen, keratin
- Keratin, RuBisCO
- Keratin, collagen
Answer : A (Collagen, RuBisCO)
Question 31: Purines have nitrogen atoms at positions.
- 1′,3′, 7′, 9′
- 1′, 5′, 7′, 9′
- 1′, 3′
- 1′,9′
Answer : A (1′,3′, 7′, 9′)
Question 32: Pyrimidines have nitrogen atoms at positions.
- 1′, 3′, 7′, 9′
- 1′, 5′, 7′, 9′
- 1′,3′
- 1′,9′
Answer : C (1′,3′)
Question 33: β – DNA which is right – handed double helix contains ______ base pairs per turn of the helix and each turn is ______ long.
- 10, 3.4 A°
- 10, 34 A°
- 11, 20 A°
- 11, 34 A°
Answer : B (10, 34 A°)
Question 34: At some points a protein molecule may be folded back on itself. This is called ______ structure and folds or coils are held together in place by ______ .
- 2°, H – bonds
- 3°, H – bonds
- 2°, Peptide bonds
- 2°, Peptide bonds
Answer : A (2°, H – bonds)
Question 35: Adult human haemolgobin consists of
- 2 subunits (α, α)
- 2 subunits (β, β)
- 4 subunits (2α, 2β)
- 3 subunits (2α, 1β)
Answer : C (4 subunits (2α, 2β))
Question 36: What will be the molecular formula of a polypeptide consisting of 10 glycine molecules when the formula of glycine is C2,H5,O2,N?
- C6 H12 O N5
- C20 H32 O11 N10
- C30 H16 O6 N10
- C25 H16 O6 N5
Answer : B (C20 H32 O11 N10)
Question 37: An unknown liquid collected from a sample of peas, is added to a beaker of water and is vigorously shaken. After few minutes, water and the unknown liquid made two separate layers. To which class of biomolecules, does the unknown liquid most likely belong?
- Polysaccharides
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Enzymes
Answer : C (Lipids)
Question 38: An a helix is the example of which type of protein structure?
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary
- Quaternary
Answer : B (Secondary)
Question 39: Which of the following is an incorrect match?
- Purines – Adenine, guanine
- Pyrimidines – Cytosine, thymine
- Structural polysaccharides – Inulin
- Storage polysaccharides – Starch
Answer : C (Structural polysaccharides – Inulin)
Question 40: Match Column – I with Column – II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| a Tetrose sugar | (i) Galactose |
| b Pentose sugar | (ii) Maltose |
| c Hexose sugar | (iii) Erythrose |
| d Disaccharide | (iv) Ribose |
- a – (v); b – (iv); c – (iii); d – (i), (ii)
- a – (iii); b – (iv); c – (v); d – (ii)
- a – (iii); b – (iv); c – (i); d – (ii)
- a – (i), (ii); b – (iv); c – (iii); d – (v)
Answer : C (a – (iii); b – (iv); c – (i); d – (ii))
Question 41: Study the given statements and select the correct answer.
(i) Cellulose is a homopolymer of glucose.
(ii) Inulin is a homopolymer of fructose.
(iii) Starch gives blue colour and glycogen gives red colour with iodine solution.
(iv) Cellulose gives no colour with iodine solution.
- Statements (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
- Statements (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct
- Statements (ii) and (iii) are correct
- All statements are correct
Answer : D (All statements are correct)
Question 42: Read the given statement and select the option that correctly identifies X and Y. In a glycogen molecule, successive glucose units are joined together by X and branches are linked together by Y.
| X | Y |
| A . 1, 4 – a – glycosidic bonds | 1, 4 – a – glycosidic acids |
| B . 1, 4 – a – glycosidic bonds | 1, 6 – a – glycosidic bonds |
| C . 1, 6 – a – glycosidic acids | 1, 4 – a – glycosidic acids |
| D . 1, 6 – a – glycosidic acids | 1,6 – a – glycosidic acids |
Answer : B (1, 4 – a – glycosidic bonds 1, 6 – a – glycosidic bonds)
Question 43: Which of the following secondary metabolites are used as drugs?
- Abrin and ricin
- Vinblastin and curcumin
- Anthocyanins
- Gums and cellulose
Answer : B (Vinblastin and curcumin)
Question 44: Match Column – I with Column – II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
| Column – I (Category) | Column – II (Secondary metabolites) |
| a Pigments | (i) Concanavalin A |
| b Terpenoids | (ii) Monoterpenes, diterpenes |
| c Alkaloids | (iii) Morphine, codeine |
| d Lectins | (iv) Carotenoids, anthocyanins |
- a – (iv), b – (ii), c – (iii), d – (i)
- a – (iv), b – (iii), c – (ii), d – (i)
- a – (i), b – (iv), c – (iii), d – (ii)
- a – (i), b – (iii), c – (ii), d – (iv)
Answer : A (a – (iv), b – (ii), c – (iii), d – (i))
Question 45: Read the given statements and select the correct option.
(i) Right end of a polysaccharide chain is called reducing end while left end is called non reducing end.
(ii) Starch can hold iodine molecules in its helical secondary structure but cellulose being non helical, cannot hold iodine.
(iii) Starch and glycogen are branched molecules.
(iv) Starch and glycogen are the reserve food materials of plants and animals respectively.
- Statements (i) and (ii) are correct
- Statements (ii) and (iii) are correct
- Only statement (iv) is correct
- All statements are correct
Answer : D (All statements are correct)
Question 46: The polysaccharides made up of glucose
- Sucrose, lactose, maltose
- Chitin, glycogen, starch
- Starch, glycogen, cellulose
- Starch, inulin, peptidoglycan
Answer : C (Starch, glycogen, cellulose)
Question 47: Read the given statements.
(i) Fructose is the sweetest sugar.
(ii) Glycine is the simplest amino acid.
(iii) Lactose is a disaccharide molecule each of glucose and galactose.
(iv) Cellulose is an unbranched chain of glucose molecules
linked by β – 1, 4 – glycosidic bond.
Which of the given statements are correct?
- (i) and (ii)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer : D ((i), (ii), (iii) and (iv))
Question 48: A β – pleated sheet organization in a polypeptide chain is an example of
- 1° structure
- 2° structure
- 3° structure
- 4° structure
Answer : B (2° structure)
Question 49: Keratin present in hair shows secondary structure known as
- Parallel β – sheet
- Antiparallel β – sheet
- α – helix
- None of these
Answer : C (α – helix)
Question 50: The regulation by an organism of chemical composition of its blood and body fluids and other aspects of its internal environment so that physiological processes can proceed at optimum rates is called
- Metabolism
- Enthalpy
- Entropy
- Homeostasis
Answer : D (Homeostasis)
Question 51: Refer the given reaction.
Enzyme A used in the reaction, belongs to which class of enzymes ?
- Dehydrogenases
- Transferases
- Hydrolases
- Lyases
Answer : C (Hydrolases)
Question 52: Enzymes that catalyse removal of groups from substrates by mechanisms other than hydrolysis, and addition of groups to double bonds, are called
- Ligases
- Lyases
- Hydrolases
- Dehydrogenases
Answer : B (Lyases)
Question 53: Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding enzymatic activity?
- It increases with increase in substrate concentration upto the saturation point.
- It is highest at optimum pH value.
- It initially decreases with increase in pH value.
- It initially increases with increase in temperature and then decreases.
Answer : C (It initially decreases with increase in pH value)
Question 54: Read the given statements and select the correct .
STATEMENT 1: Ribozymes are RNA molecules which catalyze the synthesis of certain specific RNAs and removal of introns from mRNA.
STATEMENT 2 : Ribozymes are proteinaceous enzymes.
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Answer : C (Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect)
Question 55: Enzymes catalyse the biochemical reactions ______ by activation energy .
- Lowering
- Increasing
- Unaltering
- Either A or B
Answer : A (Lowering)
Question 56: Read the given statements and select the correct option.
STATEMENT 1 : low temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation.
STATEMENT 2 : High temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive stage.
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Answer : D (Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect)
Question 57: Feed back inhibition of an enzyme is influenced by
- Enzyme itself
- External factors
- End product
- Substrate
Answer : C (End product)
Question 58: The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is called
- Competitive inhibitor
- Non – competitive inhibitor
- Activator
- Substrate analogue
Answer : B (Non – competitive inhibitor)
Question 59: Michaelis Menten Constant (Km) is equal to
- The rate of reaction
- The rate of enzymatic activity
- Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocity
- Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximum.
Answer : C (Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocity)
Question 60: Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase by malonate is an example of
- Noncompetitive inhibition
- Competitive inhibition
- Allosteric inhibition
- Negative feed back
Answer : B (Competitive inhibition)
Question 61: Dihydroxyacetone – 3 – phosphate and glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate are interconvertible. The enzyme responsible for this interconversion belongs to the cateogry of
- Isomerases
- Ligases
- Lyases
- Hydrolases
Answer : A (Isomerases)
Question 62: Holoenzyme is the complete enzyme consisting of an apoenzyme and a cofactor. Select the option that correctly identifies the nature of apoenzyme and cofactor.
- Protein Non – protein
- Non – protein Protein
- Protein Protein
- Non – protein Non-protein
Answer : A (Protein Non – protein)
Question 63: The proteinaceous molecule that joins a non – protein prosthetic group to form a functional enzyme, is called
- Apoenzyme
- co – factor
- Holoenzyme
- Isoenzyme
Answer : A (Apoenzyme)
Question 64: The inhibitor which closely resembles the substrate in its molecular structure and inhibits the enzyme activity by binding to the active site of the enzyme is called
- Feed back inhibitor
- Non – competitive inhibitor
- Competitive inhibitor
- Allosteric modulator
Answer : C (Competitive inhibitor)
Question 65: Enzymes are most functional at the temperature range of
- 15° – 25°C
- 20° – 30°C
- 30° – 50°C
- 50° – 60°C
Answer : C (30° – 50°C)
Question 66: Which of the following statements about enzymes are correct?
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three dimensional shape is key to their functions.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
(V) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy
- (i) and (v)
- (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 67: Which of the following is an example of isozyme?
- α – Amylase
- Glucokinase
- Lactate dehydrogenase
- All of these
Answer : D (All of these)
Question 68: Which of the following is the correct match ?
| Acidic amino acid | Basic amino acid | Neutral amino acid | |
| A | Glutamic acid | Lysine | Valine |
| B | Lysine | Valine | Glutamic acid |
| C | Glutamic acid | Valine | Lysine |
| D | Lysine | Glutamic acid | Valine |
Answer : A (Glutamic acid Lysine Valine )
Do share the post if you liked it. For more updates, keep logging on BrainyLads