Market Equilibrium Under Perfect Competition and Effects of Shift in Demand And Supply | Chapter 13 | Class XI | Economics |
Table of Contents
MARKET EQUILIBRIUM UNDER PERFECT COMPETITION CLASS 11 | EFFECTS OF SHIFT IN DEMAND AND SUPPLY
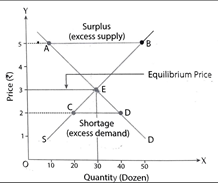
Concept of Market Equilibrium
It is defined as a state of the market when demand for a commodity is equals to its supply corresponding to a particular price. Thus, in a state of equilibrium market demand is equals to market supply of the commodity. There is neither excess demand nor excess supply. Price in the market in such situation is called equilibrium price. Quantity supplied or demanded is called equilibrium quantity.
Determination of Market Equilibrium
Market demand refers to the sum total of demand for a commodity by all the buyers in the market.
Market supply refers to the sum total of supply of a commodity by all the firms in the market.
| Price | Supply | Demand |
| 5 | 50 | 10 |
| 4 | 40 | 20 |
| 3 | 30 | 30 |
| 2 | 20 | 40 |
| 1 | 10 | 50 |
Assumptions of Market Equilibrium under Perfect Competition
- Price and quantity demanded are negatively related
- Price and quantity supplied are positively related
- Market forces operate freely without any government intervention.
Chain Effect of Shift in Demand
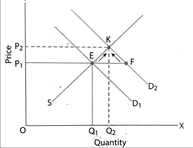
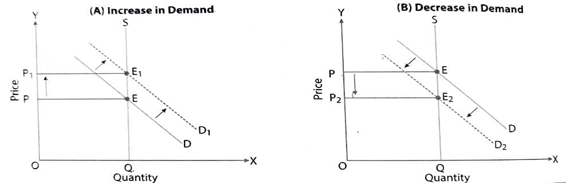
Increase in Demand
E: The point of initial equilibrium.
Increase in Demand: Demand curve shifts from D1D1 to D2D2. It causes excess demand.
It leads to rise in price from OP1 to OP2
Rise in price causes extension of supply & contraction of demand.
K: New Equilibrium Point
OP: New Equilibrium Price
OQ2: New Equilibrium Quantity.
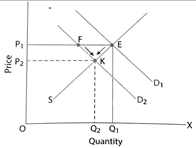
Decrease in Demand
E: The point of initial equilibrium
Decrease in Demand: Demand curve shifts from D1D1 to D2D2. It causes excess supply
It leads to fall in price from OP1 to OP2
Fall in price causes extension of demand & contraction of supply
K: New Equilibrium Point
OP2: New Equilibrium Price
OQ2: New Equilibrium Quantity.
Chain Effect of Shift in Supply
Increase in Supply
E: The point of initial equilibrium
Increase in Supply: supply curve shifts from S1S1 to S2S2. It leads to fall in price from OP1 to OP2
Fall in price causes extension of demand and contraction of supply
K: New Equilibrium Point.
OP1: New Equilibrium Price
OQ2: New Equilibrium Quantity.
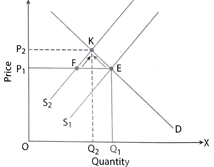
Decrease in Supply
E: The point of initial equilibrium
Decrease in supply: supply curve shifts from S1S1 to S2S2
It leads to rise in price from OP1 to OP2
K: New equilibrium point
OP1: New equilibrium price
OQ2: New equilibrium quantity.
Some Exceptional Situations
Effect of Change in Demand when Supply in Perfectly Elastic
When the supply curve is perfectly elastic i.e parallel to X-axis, a change in demand does not affect the equilibrium price. It only changes the equilibrium quantity.
Effect of Change in Demand when Supply is Perfectly Inelastic
When the supply curve is perfectly inelastic i.e parallel to Y-axis, a change in demand does not affect the equilibrium quantity. It only changes the equilibrium price.
Effect of Change in Supply when Demand is Perfectly Elastic
When the demand curve is perfectly elastic i.e parallel to X-axis, a change in supply does not affect the equilibrium price. It only changes the equilibrium quantity.
Effect of Change in Supply when Demand is Perfectly Inelastic
When the demand curve is perfectly inelastic i.e parallel to Y-axis, a change in supply does not affect the equilibrium quantity. It only changes the equilibrium price.
RELATED
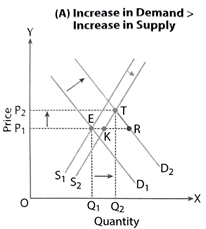
Simultaneously Increase in Demand and Supply
Increase in Demand > Increase in Supply
- It causes excess demand
- Accordingly, equilibrium price rises and equilibrium quantity increases.
- Rise in price causes contraction of demand & extension of supply
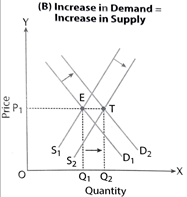
Increase in Demand = Increase in Supply
- It keeps supply and demand in a state of equilibrium corresponding to the same price.
- There is no change in equilibrium price
- Equilibrium quantity increases.
Increase in Demand< Increase in Supply
- It leads to excess supply.
- Accordingly, equilibrium price falls and equilibrium quantity increases.
- Fall in price causes extension of demand and contraction of supply
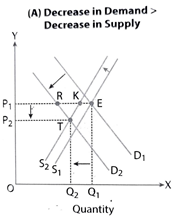
Simultaneously Decrease in Demand and Supply
Decrease in Demand > Decrease in Supply
- It is a situation of excess supply.
- Equilibrium price tends to fall & equilibrium quantity decreases.
- Because of a fall in price, there is extension of demand & contraction of supply.
Decrease in Demand = Decrease in Supply
- It keeps Supply & Demand in a state of
- equilibrium corresponding to the same price.
- There is no change in equilibrium price
- Equilibrium quantity reduces from OQ1 to OQ2
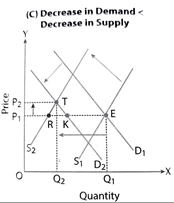
Decrease in Demand < Decrease in Supply
- It is a situation of excess demand.
- Equilibrium price rises & equilibrium quantity decreases.
- Because of rise in price, there is contraction of demand and extension of supply.
Do share the post if you liked the notes of Market equilibrium. For more updates, keep logging on BrainyLads.