MCQ of Solutions | Chapter 2 | Chemistry | Class 12 | CBSE |
MCQ of Solutions | Multiple Choice Questions of Solutions |
MCQ of Solutions
Question 1: State the main advantage of molality over molarity as the unit of concentration.
- Molality does not change with change in temperature
- Molality changes with temperature
- Molarity changes with temperature
- None of these
Answer: A (Molality does not change with change in temperature )
Question 2: Brass is
- Solid Solution
- Liquid Solution
- Gas solution
- All of these
Answer: A (Solid Solution)
Question 3: Which of the following is an example of solid in gas solution?
- Humidity in air
- Iodine vapour in air
- Alloys
- Air
Answer: B (Iodine vapour in air)
Question 4: Write the relation between normality and molarity of a given solution of H2SO4 ?
- Normality = 2 x Molarity
- Molarity = 2 x Normality
- Normality = 3/4 Molarity
- Molarity = 1/2 Normality
Answer: A (Normality = 2 x Molarity)
Question 5: What is sum of mole fraction of all the components in a three component system?
- x1 + x2 + x3 = 2
- x1 + x2 + x3 = 1
- x1 + x2 = 1
- x1 + x3 = 1
Answer: B (x1 + x2 + x3 = 1 )
Question 6: At equilibrium the rate of dissolution of a solid solute in a volatile liquid solvent is..
- zero
- less than the rate of crystallisation
- equal to the rate of crystallisation
- greater than the rate of crystallisation
Answer: C (Equal to the rate of crystallisation )
Question 7: What do you mean by saying that molality of a solution is 0.1?
- 0.1 mol of solute is dissolved in 1000kg of solvent
- 0.1 mol of solute is present in 100 ml of solution
- 0.1 mol of solute is dissolved in 1000g of solvent
- None of these
Answer: C (0.1 mol of solute is dissolved in 1000 g of solvent)
Question 8: Which has the least freezing point?
- 1% Sucrose
- 1% NaCl
- 1% CaCl2
- 1% Glucose
Answer: C (1% CaCl2 )
Question 9: Which of the following is not a colligative property?
- Depression in freezing point
- Osmotic Pressure
- Elevation in boiling point
- Increase in freezing point
Answer: D (Increase in freezing point)
Question 10: In which of the following condition reverse osmosis takes place ?
- E ext > Osmotic pressure
- E ext = Osmotic pressure
- E ext < Osmotic pressure
- None of these
Answer: A (Eext > Osmotic Pressure)
You may also read MCQ of The Solid State, MCQ of Solutions, MCQ of Electrochemistry, MCQ of Chemical Kinetics, MCQ of Surface Chemistry, MCQ of General Principles and Processed of Isolation of Elements, MCQ of the p-Block Elements, MCQ of the d-And f-Block Elements, MCQ of Coordination Compounds, MCQ of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, MCQ of Alcohols, Phenols and Ether, MCQ of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, MCQ of Amines, MCQ of Biomolecules, MCQ of Polymers, MCQ of Chemistry in Everyday Life
Question 11: Molarity of a given orthophosphoric acid solution is 3M. Its normality is
- 0.3 N
- 9 N
- 1 N
- 3 N
Answer: B (9 N)
Question 12: What is ebullioscopic constant.
- Elevation in boiling point that take place when molarity of the solution is unity.
- Depression in freezing point that take place when molality of the solution is unity
- Elevation in boiling point that take place when molality of the solution is unity.
- Depression in freezing point that take place when molarity of the solution is unity
Answer:C (Elevation in boiling point that take place when molality of the solution is unity.)
Question 13: Two liquids A and B on mixing produce a warm solution. Which type of deviation from Raoult’s law does it show?
- negative deviation.
- positive deviation
- Ideal solution
- All of these
Answer: A (Negative deviation)
Question 14: A beaker contains a solution of substance A. Precipitation of substance A takes place when small amount of A is added to solution. The solution is ……..
- Saturated
- Unsaturated
- Supersaturated
- None of these
Answer: C (Supersaturated)
Question 15: Maximum amount of a solute that can be dissolved in a specified amount of given liquid solvent does not depend upon
- Pressure
- Temperature
- Nature of solute
- Nature of solvent
Answer: A (Pressure)
Question 16: What happens when blood cells are placed in pure water?
- blood cells shrink
- blood cells swell and may even burst.
- Both of these
- None of these
Answer: B (Blood cells swell and may even burst )
Question 17: When is the value of van’t Hoff factor more than one?
- when solute undego association in the solution
- when the solute undergo dissociation in the solution
- when solute is volatile
- None of these
Answer: B (When the solute undergo dissociation in the solution)
Question 18: Which one has a lowest freezing point?
- 2 M glucose solution
- 1.5 M glucose solution
- 1 M glucose solution
- All of these
Answer: A (2 M glucose solution)
Question 19: Isotonic solutions are solutions having the same
- Vapour pressure
- Surface tension
- Osmotic pressure
- Viscosity
Answer: C (Osmotic Pressure)
Question 20: How is the colligative property of solution changed when a solute in solution undergoes association
- Increases
- Remain same
- Become twice
- Decreases
Answer: D (Decreases)
Question 21: The value of Henry’s constant is…..
- greater for gases with higher solubility
- greater for gases with lower solubility
- constant for all gases
- not related to the solubility of gases
Answer: B (Greater for gases with lower solubility)
Question 22: Vapour pressure of a dilute aqueous solution of glucose is 750 mm of mercury at 373 K. The mole fraction of solute is
- 1 / 76
- 1 / 7.6
- 1 / 38
- 1 / 10
Answer: A (1 / 76) [ Hint : ps = pº1 ( 1- x2) ]
Question 23: The decreasing order of osmotic pressure of 10 g glucose (P 1), 10 g urea (P2) and 10 g sucrose (P3) at 273 K when dissolved in 250 mL of water separately is
- P1 > P2 > P3
- P2 > P3 > P1
- P2 > P1 > P3
- P3 > P2 > P1
Answer: C (P2 > P1 > P3 ) [ Hint : P ∝ 1 / Molar mass ]
Question 24: An azeotropic mixture of two liquids has boiling point lower than either of them when it
- shows negative deviation from Raoult’s law
- shows no deviation from Raoult’s law
- shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law
- is saturated
Answer: C (Shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law)
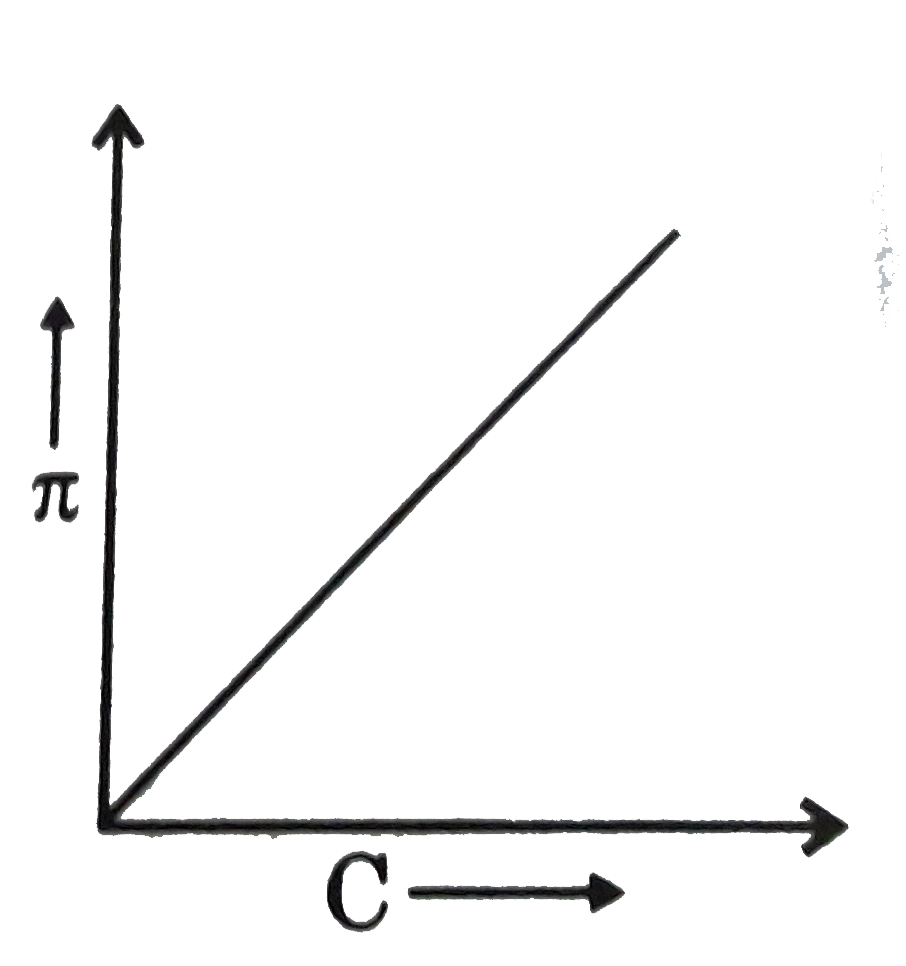
Question 25: A graph showing the variation of osmotic pressure versus molar concentration of an aqueous solution at temperature T is given below; the slope of the line represent
- solution constant R
- absolute temperature T
- RT
- degree of ionization of solute
Answer: C (RT)
Question 26: The osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous solution of NaCl is …… osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous solution of glucose
- equal to
- less than
- half of
- nearly double
Answer: D (Nearly double)
Question 27: Which of the following 0.1 M aqueous solution is likely to have the highest boiling point?
- Na2SO4
- KCl
- Glucose
- Urea
Answer: A (Na2SO4)
Question 28: Increasing the temperature of an aqueous solution will cause
- decrease in molality
- decrease in molarity
- decrease in mole fraction
- decrease in % w/w
Answer: B (Decrease in molarity )
Question 29: Van’t Hoff factor for 0.1 M ideal solution is
- 0.1
- 1
- -0.01
- none of these
Answer:B (1)
Question 30: Which of the following will show negative deviation from Raoult’s law?
- Acetone – benzene
- Acetone – ethanol
- Benzene – methanol
- Acetone – chloroform
Answer: D (Acetone – chloroform )
Do share the post if you liked it. For more updates, keep logging on BrainyLads