Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 | Notes | Science | Term 2 |
Table of Contents
Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 | Notes | Science |
#Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10
Matter around us is present in the form of element, compound and mixtures.
Element contains atom of only one type.
At present, 114 elements are known. Around 1800 , only 30 elements were known.
As different elements were being discovered, scientist gathered more and more information about new discovering elements. Scientist find it difficult to learn about properties of all known elements. So they started looking for pattern in their properties on the basis of which they could study properties of element with ease.
Several attempt were made by scientist in order to classify element according to their properties. The earliest attempt was grouping the then known element as metal and non metal.
Dobereiner’s Triads
- In 1817, Johann Wolfgang Doberenier, a German chemist tried to classify element with similar properties into groups.
- Some groups having three element each were identified by him. He called these groups as triads. He showed when elements in groups are written in increasing order of their atomic mass, the atomic mass of middle element of triad will be equal to average atomic mass of other two .
- These elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic mass in downward direction.
Limitations :
Dobereiner could find only three triad out of element known at that time. Hence, this system of classification into triads did not proved very successful. Moreover, the law failed for very low and very high mass element.
Newland’s Law of Octaves
The attempt made by Dobereiner regarding the classification of elements encouraged the other scientist to correlate the properties of element with respect to their atomic mass. In 1866, John Newland, an English scientist arranged the element in increasing order of atomic mass starting from lower atomic mass (hydrogen) and ended at Thorium which was 56th element. It was found by Newland that every eighth element has properties similar to that of first. He compare this to octaves found in music. Therefore, he called it law of octaves and it is considered as Newland law of octaves.
Limitations:
- The law was applicable only upto calcium. After calcium the law was not valid since every eighth element does not possess similar properties to that of first one.
- The law was valid only for element with lighter mass.
- The law was valid only for element with lighter mass.
- Newland supposed that only 56 elements existed in nature and there is no possibility for further elements to be discovered in future. But later few new elements were discovered which did not fit into his table.
- He adjusted two elements in same slot in order to adjust element into his table. In order to do this he adjusted some unlike elements under same note like cobalt and nickel are placed in same group with bromine, fluorine and chlorine which has properties very different to cobalt and nickel.
- Iron which has properties similar to some other elements such as cobalt and nickel has been placed far away from these elements.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
Even after the rejection of Newland law of octaves, many scientists continued to search for pattern that correlate to the properties of element with their atomic mass. The main credit for classifying element on the basis of their fundamental property, i.e., atomic mass goes to Dmitri Lvanovich Mendeleev, a Russian chemist. The arrangement of element he proposed is called Mendeleev periodic table.
- At the time when Mendeleev started his work, only 63 elements were known.
He correlated the atomic mass of element and their physical and chemical properties.
Among chemical properties, he mainly focused on compound that are formed by element with hydrogen and oxygen. - He considered hydrogen and oxygen as these are most reactive element and react with most elements. According to him, formula of hydrides and oxides of element are basic property of element for their classification.
- He took 63 cards and properties of 1 element on each card. He then sorted element with similar properties and pinned them on wall. He found most of the elements got a place in periodic table and were arranged in pattern in increasing order of atomic masses.
- On this basis, he formulated a law which stated that properties of element are periodic function of their atomic masses.
- The periodic table proposed by him was published in German journal in 1872. The table consists of 6 periods and 8 groups.
Achievements of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- He left some Gaps in his periodic table. Instead of looking these gaps as defects he predicted the existence of some elements that had not been discovered at that time. He named those elements by prefixing using Sanskrit numeral eka.
- Like Scandium, Gallium and Germanium that had been discovered later ere found to have properties similar to eka- boron, eka- silicon and eka- aluminium respectively.
- It was an extraordinary success of him that led other chemist to not only to accept his table but to recognize him as a originator of concept on what it is based.
- Noble gases like helium, Argon were also been discovered later as they are inert , they are present in low concentration in atmosphere. But when they were discovered they were able to fit in his periodic table in a new group without disturbing the existing order.
- There are some instances where Mendeleev had placed element with greater atomic mass with slightly lower atomic mass. This sequence was inverted in such a way that elements having similar properties can be grouped together.
Limitations of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
No fixed position can be given to hydrogen as it is a diatomic molecule and forms covalent bond. This was the first limitation of his periodic table that he could not assign correct position to hydrogen in his table.
Although , Isotopes have different chemical properties they are placed in same position with Hydrogen.
No distinction regarding metals and non metals were proposed by him.
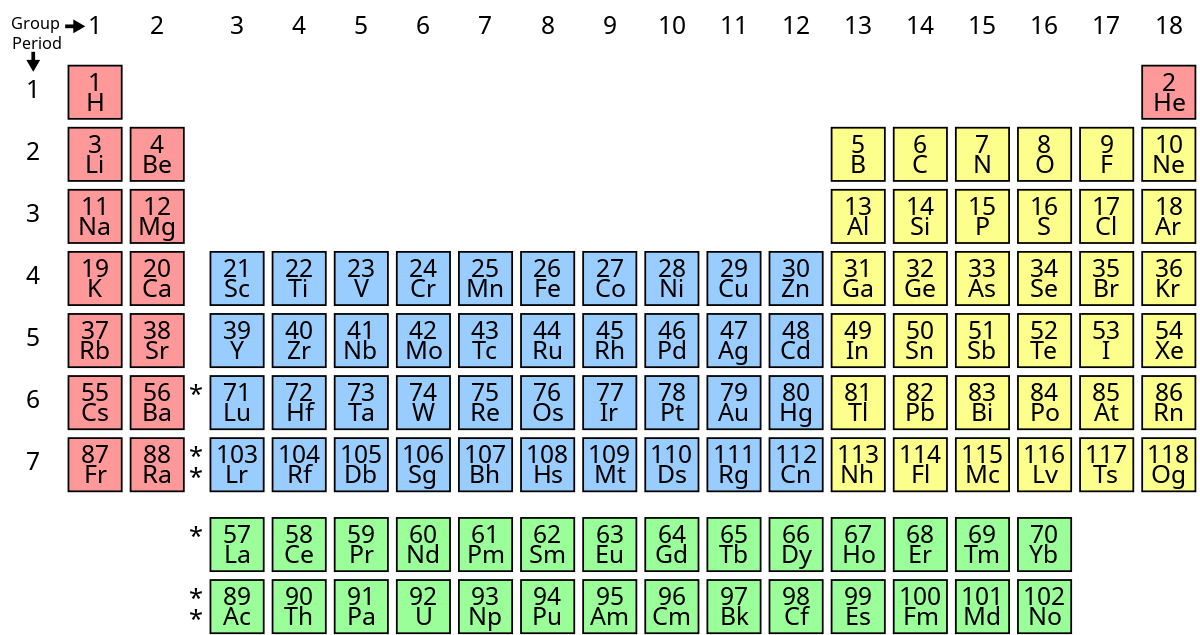
Modern Periodic Table
- It was made by Henry Moseley. In his periodic table, he showed that atomic number is more fundamental property of an element as compared to atomic mass.
- Modern periodic table states properties of an element are periodic function of their atomic number.
- Atomic number gives us number of proton in a nucleus and properties of element can be understood more easily when elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic number (Z).
- It has 18 groups and 7 periods.
- It has made the study of chemistry more systematic and easier.
Element present in one group have same no of valance electron (from top to bottom)
No of shell increases while moving down the group.
No of valance shell increases by one unit as atomic no increases by one unit (from top to bottom)
Position of an element in Modern periodic table tells us about its chemical reactivity.
Valance electron determine the kind and no of bond formed by an element.
Limitations: Lanthanoids and actinoids has not yet got any satisfactory place. Hydrogen position is also yet undecided.
Trends in Modern Periodic Table
Valency: As we move from top to bottom valance remain same, number of valence electrons remain same resulting in same valency and as we move from left to right valency increases upto group 14 and then decreases.
Valence Electron: As we move from top to bottom valance electron remain same and as we move from left to right valance electron increases.
Atomic Size: As we move from top to bottom , atomic size increases due to increase in no of shell . This increases the distance between outermost electron which leads to increase in atomic size in spite of increase in nuclear charge. As we move from left to right atomic size decreases due to increase in nuclear charge which tends to pull the electron closer to nucleus and reduces the size of the atom.
Metallic and Non metallic character: A zig zag line of metalloid separate metals that are on left side from the non metals that are on the right side of the periodic table. As we move from left to right, metallic character decreases while as we move down the group, it decreases.
As we move from left to right, increase in non metallic character is observed due to increase in electronegativity while it decreases down the group due to decrease in electronegativity of atoms.
Question: The elements X, Y and Z have the electronic configuration as given below:
X = 2,7 Y = 2,8,5 Z = 2,8,8
Determine the position of the elements as per the modern periodic table.
Answer: The element X has 7 valence electron thus it must belongs to group 17. Since X has two occupied shells it belongs to 2nd period.
The element Y has 5 valence electron thus it must belongs to group 15. Since Y has three occupied shells it belongs to 3rd period.
The element Z has 8 valence electron thus it must belongs to group 18. Since Y has three occupied shells it belongs to 3rd period.
Question: What is meant by group and period in the periodic table?
Answer: The vertical columns in the modern as well as in Mendeleev’s periodic table are generally referred as groups whereas the horizontal rows in the modern as well as in Mendeleev’s periodic table are periods.
Question: The atomic radii of the group 1 elements are given as below in a random manner:
| Element | Na | Li | Rb | Cs | K |
| Atomic Radius (pm) | 186 | 152 | 244 | 262 | 231 |
(a) Arrange the given elements in the increasing order of atomic radius.
(b) Explain the variation in atomic size as you go down the group.
(c) Name the elements having smallest and largest atoms.
Answer: (a) The accurate order of increasing size is as follows: Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs
(b) The atomic size increases as we move down the group due to increase in the number of shells.
(c) Li has smallest whereas Cs has the largest size.
Question : What do you think could be the possible reason for placing noble gases in separate group?
Answer: These are considered as very inert and chemically unreactive since they have completely filled valence subshells. Thus noble gases are placed in a separate group.
Question : The atomic number of three elements A,B and C are given as below in the table:
| Element | Atomic Number |
| A | 5 |
| B | 7 |
| C | 10 |
Answer the following questions:
(a) Identify the group number of given elements as per the modern periodic table.
(b) Also determine the periods of these elements in the Modern periodic table.
(c) Which among these given elements is considered to have the smallest atomic radius. Give reason.
Answer: (a)
| Element | A | B | C |
| Group No | 13 | 15 | 18 |
(b) All these three elements belong to the second period.
(c) C is the smallest element since atomic size decreases while moving from left to right.
———————————-
# Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10
Do share this post if you liked Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Notes. For more updates, keep logging on BrainyLads.